Volatility Trading Strategies

Volatility trading is an advanced approach to trading.
These strategies are primarily used in options trading, but they can also be applied to other financial instruments.
Focusing on the magnitude, speed, or variation of price movements – rather than their direction – enables traders to potentially profit in both up and down markets.
It’s gained popularity among institutional traders due to its potential in various market environments.
It can generate returns independent of traditional asset classes, which creates an opportunity for various institutions to create value for their clients.
For non-institutional traders, volatility trading can generate returns independent of standard directional strategies.
Key Takeaways – Volatility Trading Strategies
- Market-neutral opportunity
- Volatility trading can be profitable in both up and down markets.
- Offers diversification benefits and hedging potential against market unknowns.
- Multiple strategies available
- Traders can use various approaches like mean reversion, risk premium harvesting, and volatility arbitrage to take advantage of different market environments and volatility patterns.
- Specific learning and training is required, as volatility is a specialized skill set
- Risk management
- Position sizing, risk management, and stress testing are important for successful volatility trading.
What is Volatility?
Volatility refers to the degree of variation in the price of a financial instrument over time.
It’s typically measured by the standard deviation of returns and is often expressed as a percentage.
High volatility indicates rapid and large price fluctuations, whereas low volatility suggests more stable and predictable price movements.
Why Trade Volatility?
Trading volatility offers several advantages:
- Market-neutral strategy – Volatility trades can be profitable regardless of whether the market is moving up or down.
- Diversification – Volatility often has a low correlation with traditional asset classes, providing portfolio diversification benefits.
- Hedging – Volatility strategies can be used to hedge against market unknowns and potential downturns.
In general, volatility is important because of:
- Risk assessment – volatility is a component of risk
- Pricing of derivatives
- Identification of trading opportunities
- Portfolio diversification
Understanding and effectively using volatility can give traders an edge in the market.
Volatility Trading Strategies
Volatility Mean Reversion
This strategy is based on the assumption that volatility tends to revert to its long-term average.
Traders can:
- Sell volatility when it’s abnormally high
- Buy volatility when it’s abnormally low
Implementation often involves trading options or OTC derivatives.
The main drawback with this type of strategy is that it tends to be more tactical.
Unlike passive strategies, volatility mean reversion opportunities can be fleeting.
For example, if S&P 500 volatility is priced at 37% when its long-run average is 15%, that might be a great trade, but what happens when that opportunity dries up and other ones aren’t there?
Volatility Risk Premium Harvesting
This strategy exploits the tendency for implied volatility to be higher than realized volatility over the long term. Traders can:
- Sell options or variance swaps when implied volatility is high
- Buy back the positions when implied volatility decreases or when options expire
Volatility Term Structure Trading
The volatility term structure represents the relationship between implied volatility and time to expiration.
Traders can profit from changes in the shape of the term structure by:
- Trading calendar spreads
- Exploiting differences between short-term and long-term implied volatility
Volatility Arbitrage
Volatility arbitrage involves identifying and exploiting pricing discrepancies in related volatility instruments.
Strategies here include:
- Options vs. underlying arbitrage
- Cross-asset volatility arbitrage
- Volatility surface arbitrage
With cross-asset vol arb, this is where multi-asset Greeks become important for analysis.
Gamma Trading
Gamma trading focuses on profiting from large price movements in the underlying asset.
Traders can:
- Buy options with high gamma when expecting increased volatility
- Dynamically hedge the position to capture profits from price swings
Related: Gamma Scalping
Vega Trading
Vega measures an option’s sensitivity to changes in implied volatility.
Vega trading strategies involve:
- Taking positions with positive or negative vega exposure
- Profiting from changes in implied volatility while managing directional risk
Straddle and Strangle Strategies
A long straddle involves simultaneously buying a call and a put option with the same strike price and expiration date.
Long Straddle
- Buy a call and a put option at the same strike price and expiration date.
- This strategy profits from significant price movements in either direction.
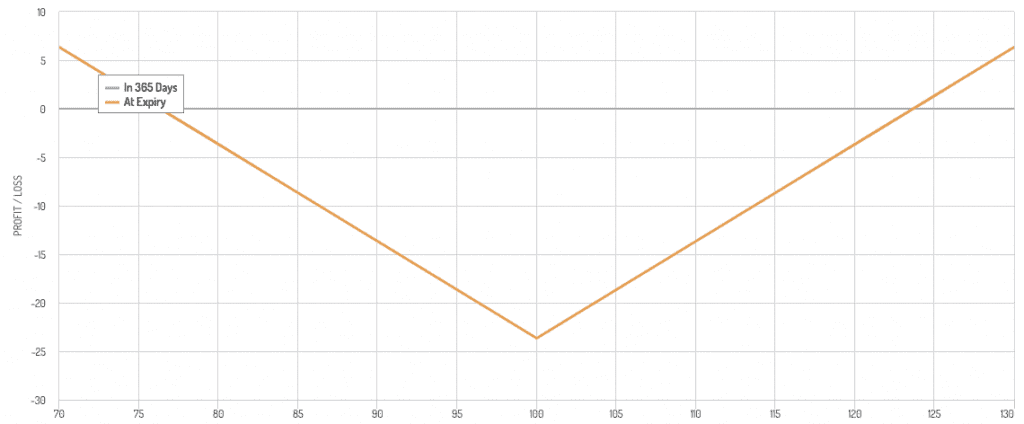
Long Strangle
- Buy a call and a put option at different strike prices but the same expiration date.
- Less expensive than a straddle but requires a larger move to be profitable.
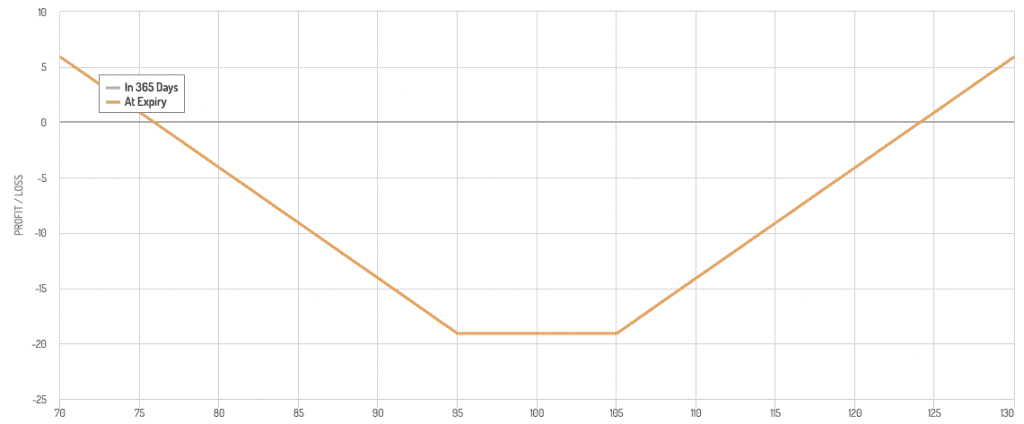
Volatility Dispersion Trading
This strategy involves trading the volatility of an index against the volatility of its constituent components.
Dispersion Trading
- Long volatility on individual stocks while shorting the index volatility or vice versa.
- Profits from the divergence in volatility between the index and its components.
Correlation Trading
Correlation trading strategies are based on the relationships between different assets.
Statistical Arbitrage
- Exploit statistical mispricing of one or more assets based on the assumption that their prices will revert to a historical norm.
Volatility Momentum
This strategy involves trading based on the momentum of volatility itself.
How a day trader might approach volatility momentum:
- Enter trades based on breakouts from historical volatility ranges.
- Use technical indicators to identify and trade periods of increasing or decreasing volatility.
Volatility of Volatility
Volatility of volatility (vol-of-vol) strategies focus on trading the fluctuations in volatility itself.
Traders use instruments like options on VIX futures to profit from changes in market volatility expectations.
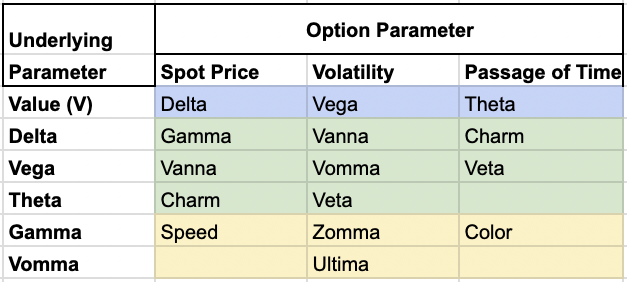
Vol of vol strategies often use second-order and third-order vol Greeks, like Vanna, Vomma, Veta, Zomma, and Ultima.
Tail Risk Hedging
This strategy involves protecting portfolios against extreme market moves.
Buying Out-of-the-Money Options
- Purchase options far out of the money to hedge against rare but severe market movements.
Skew Trading
This strategy involves trading based on the skewness of the options market.
Trading Skew
- Exploit differences in implied volatility between out-of-the-money calls and puts.
- Use strategies like risk reversals (buying a call and selling a put with the same delta) to benefit from skew changes.
As this chart shows, volatility can vary a lot depending on the strike price, which is why it’s often called a “volatility smile”:
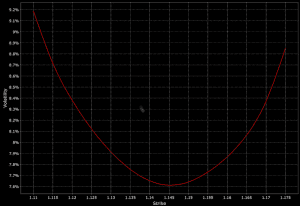
The basic idea is to be long cheap vol and short pricier vol.
When to Use
- When there’s a significant difference in implied volatility between strikes
- To take advantage of market inefficiencies
Risks
- Complex execution
- Requires accurate volatility forecasting
Iron Condor and Iron Butterfly
These strategies involve trading a range of prices and benefit from low volatility.
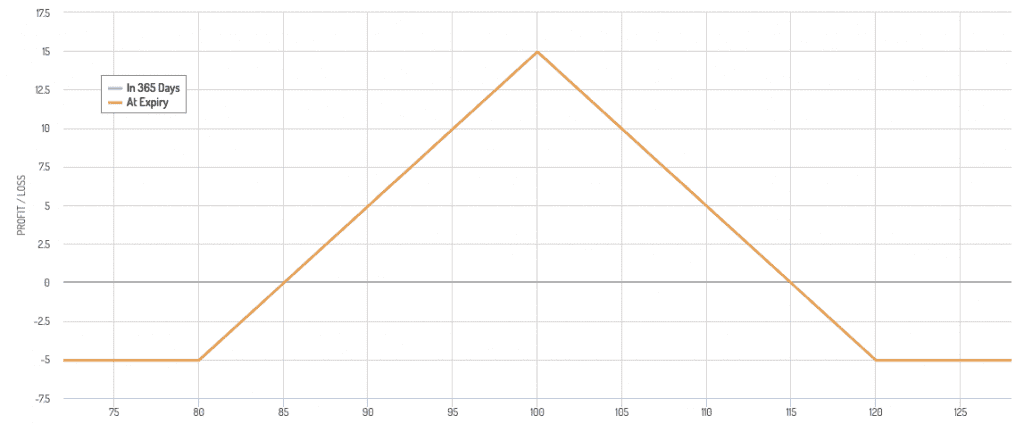
Iron Condor
- Sell out-of-the-money call and put options, and buy further out-of-the-money call and put options to limit risk.
- Profits from the underlying staying within a certain range.
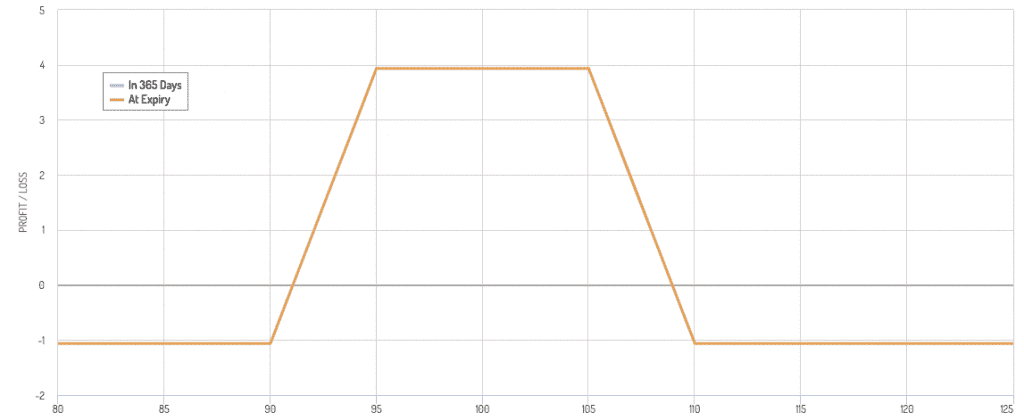
Iron Butterfly
- Sell a straddle (at-the-money call and put) and buy a strangle (out-of-the-money call and put) to limit risk.
- Profits from the underlying staying near the strike price.
Delta Hedging
This strategy involves maintaining a delta-neutral portfolio to manage risk.
Dynamic Hedging
- Continuously adjust the portfolio’s delta to remain neutral as the price of the underlying asset changes.
- Used to manage the risk of a large position in options.
Volatility Risk Premium
The volatility risk premium (VRP) refers to the tendency for implied volatility to be consistently higher than realized volatility over time.
This premium exists because traders are generally willing to pay extra for protection against market unknowns.
Options contracts provide access to the VRP.
To capture the VRP, traders typically use strategies that involve selling options or volatility-related instruments when implied volatility is high and buying them back when it decreases.
Common approaches include:
- Selling out-of-the-money options – Writing puts or calls that are less likely to be exercised. An example would be selling OTM puts on assets you’d be willing to buy anyway if it got down to a certain price.
- Covered call or put – Selling options at a price where you’d be willing to cover your position.
- Short straddles or strangles – Simultaneously selling both call and put options at the same (straddle) or different (strangle) strike prices.
- Selling variance swaps – These OTC derivatives allow direct exposure to the difference between implied and realized variance.
- Short VIX futures – Betting on a decrease in the VIX index, which often trades at a premium to realized volatility.
These strategies can generate quality returns over time, but they also carry large risks, particularly during market turbulence.
Short Volatility Strategies
These strategies involve selling options to profit from a decrease in implied volatility or time decay.
Examples
- Short straddle
- Short strangle
- Iron condor
When to Use
- Expecting volatility to decrease
- In high implied volatility environments
Risks
- Unlimited potential losses if the underlying asset moves significantly
- Requires careful risk management
Using Volatility-Based Betting Strategies
Volatility Analysis Tools
To effectively use volatility-based strategies, traders use various concepts/metrics:
- Historical Volatility (HV) – Measures past price fluctuations
- Implied Volatility (IV) – Reflects the market’s expectation of future volatility
- Volatility Index (VIX) – A real-time market index representing the market’s expectation of 30-day forward-looking volatility
Considerations
When implementing these strategies, traders should consider:
- Current market conditions
- Historical volatility patterns
- Upcoming events that may impact volatility
- Correlation between assets
- Liquidity of the options market
Risk Management
Proper risk management is important when using volatility-based strategies:
- Set clear stop-loss levels for those who use them (longer-term trading styles tend to not)
- Use position sizing appropriate to your risk tolerance
- Regularly monitor and adjust positions
- Diversify across multiple uncorrelated assets
Advanced Volatility-Based Betting Strategies
1. Volatility Arbitrage
This strategy involves exploiting discrepancies between implied and realized volatility.
Techniques
- Statistical arbitrage
- Dispersion trading
- Volatility surface trading
Challenges
- Requires sophisticated modeling and execution
- Specific skill set that requires training and specific technology
- High transaction costs
- Limited opportunities
2. Volatility Term Structure Strategies
These strategies exploit the relationship between short-term and long-term implied volatilities.
Techniques
Challenges
- Complex risk profile
- Requires accurate forecasting of volatility term structure changes
Pros and Cons of Volatility-Based Betting Strategies
Pros
- Potential to profit in various market conditions
- Can be used for both speculation and hedging
- Offers unique diversification benefits
- Allows for precise expression of market views
Cons
- Often involves complex calculations and modeling
- Can be expensive due to option premiums
- Requires active management and monitoring
- Potential for significant losses if not properly managed
Case Studies: Successful Volatility-Based Betting
The VIX Explosion of February 2018
In February 2018, the VIX experienced its largest one-day spike in history.
Traders who had implemented long volatility strategies, such as buying VIX calls or using long straddles on the S&P 500, saw significant profits.
Key Takeaways
- The importance of having some long volatility exposure as a hedge, particularly for portfolios long risk assets
- The potential for extreme volatility events to occur unexpectedly
Volatility Arbitrage During the 2020 COVID-19 Crash
During the market turmoil of March 2020, some hedge funds successfully used volatility arbitrage strategies. They profited from the disconnect between implied volatility in different markets and assets.
Key Takeaways
- Opportunities for volatility arbitrage increase during periods of market stress
- The importance of having a robust risk management framework in place
The Future of Volatility-Based Betting Strategies
As financial markets evolve, so too will volatility-based betting strategies.
Several trends are likely to shape the future of these strategies:
1. Machine Learning and AI
Algorithms will increasingly be used to identify volatility patterns and execute trades.
This may lead to more efficient markets but also create new opportunities for those with superior technology.
2. New Volatility-Based Products
The development of new financial products, such as more sophisticated volatility ETFs or blockchain-based volatility derivatives, could provide traders with additional ways to use these strategies.
3. Regulatory Changes
Increased scrutiny of complex financial instruments may impact the availability and execution of certain volatility-based strategies.
Traders will need to stay informed about regulatory developments.
4. Integration with Other Strategies
Volatility-based betting is likely to become more integrated with other trading approaches, such as momentum or value strategies, to create more robust and diversified trading systems.
Types of Volatility
Understanding the different types of volatility is important for developing effective trading strategies.
Historical Volatility
Historical volatility (HV) measures the actual price fluctuations of an asset over a specific period in the past.
It shows how volatile an asset has been and can be used to estimate future volatility.
Implied Volatility
Implied volatility (IV) is derived from option prices and represents the market’s expectation of future volatility – i.e., discounted volatility.
It’s a forward-looking measure and is often considered more relevant for trading purposes than historical volatility.
Realized Volatility
Realized volatility (RV) measures the actual volatility that occurs over a specific period.
It is calculated using high-frequency data and is often compared to implied volatility to identify potential trading opportunities.
Volatility Spreads
Volatility spreads are option strategies that try to profit from changes in implied volatility.
These spreads involve simultaneously buying and selling options with different strike prices or expiration dates to create a position that is sensitive to volatility changes.
Examples of volatility spreads include:
Calendar Spreads
Involve buying and selling options with the same strike price but different expiration dates.
Traders profit from changes in the volatility term structure.
Butterfly Spreads
Consist of buying one option at a lower strike, selling two at a middle strike, and buying one at a higher strike.
This strategy benefits from a decrease in implied volatility.
Iron Condors
Combine a bull put spread and a bear call spread.
Traders profit when implied volatility decreases and the underlying asset remains within a specific range.
Vega-Weighted Spreads
Adjust the number of contracts traded to create a position with a specific vega exposure, allowing traders to isolate volatility risk.
Skew Trades
Exploit differences in implied volatility between out-of-the-money calls and puts, often using risk reversals.
Overall
These strategies allow traders to take specific positions on volatility while managing other option Greeks and directional risk.
They require careful management and a solid understanding of options dynamics.
Volatility Trading Instruments
Traders can access volatility through various financial instruments:
Volatility Index (VIX) Futures and Options
The CBOE Volatility Index (VIX), also known as the “fear index,” is a popular measure of market expectations of near-term volatility.
Traders can use VIX futures and options to speculate on or hedge against volatility in the S&P 500 index.
Variance Swaps
Variance swaps are over-the-counter derivatives that allow traders to speculate on the difference between realized and implied volatility.
They provide direct exposure to volatility without the complexities of managing option positions.
Options Strategies
Various option strategies can be employed to trade volatility, including:
- Straddles and strangles
- Butterflies and iron condors
- Volatility spreads
Volatility ETFs and ETNs
Exchange-traded funds (ETFs) and exchange-traded notes (ETNs) linked to volatility indices provide easier access to volatility trading for day traders.
These products often suffer from decay due to contango in the futures markets and are generally more suitable for short-term, intraday trading only.
Risk Management in Volatility Trading
Position Sizing
Careful position sizing is essential to limit potential losses and be sure that no single trade can have a catastrophic impact on the overall portfolio.
Stop-Loss Orders
Using stop-loss orders can help limit downside risk, especially when trading leveraged volatility products.
Protective Options
Using protective options can predefine your downside.
Diversification
Diversifying across different volatility strategies, timeframes, and underlying assets can help reduce overall portfolio risk.
Volatility strategies can be diversified with others.
Stress Testing
Regularly stress-testing volatility trading strategies under various market scenarios can help identify potential weaknesses and areas for improvement.
Challenges in Volatility Trading
Complexity
Volatility trading often involves complex mathematical models, unique sensitivities and parameters (e.g., Greeks), and sophisticated trade structures.
They can require a high level of expertise and market knowledge.
Liquidity Risk
Some volatility instruments, particularly OTC derivatives, may have limited liquidity.
This can lead to wider bid-ask spreads and potential difficulties in executing trades.
Regulatory Risk
The regulatory landscape for volatility trading, especially concerning certain derivatives, is subject to change, which can impact trading strategies and market access.
Model Risk
Volatility trading strategies often rely on mathematical models that may not accurately capture all market dynamics.
Accordingly, this can lead to potential losses if model assumptions are incorrect or variables are missing from the analysis.
Technological Considerations
Vol trading at the institutional level tends to be very technologically intensive.
High-Frequency Trading
Many volatility trading strategies benefit from high-frequency trading capabilities to exploit short-term market inefficiencies and manage risk effectively.
Longer-term vol strategies are still possible.
Risk Management Systems
Strong risk management systems are essential for monitoring and controlling the various risks associated with volatility trading.
This is generally extremely difficult to do by hand or discretionarily.
Data Analysis and Testing
Advanced data analysis and backtesting/stress testing are important for developing and refining volatility trading strategies.
Conclusion
Volatility trading offers unique opportunities for sophisticated traders to profit from market unknowns and price fluctuations.
Understanding the various types of volatility, trading instruments, and strategies available, can allow traders to develop approaches that align with their risk tolerance and market outlook.
Note that volatility trading carries significant risks and requires a deep understanding of market dynamics, options pricing, and risk management techniques.
Successful volatility traders typically combine high levels of market knowledge with disciplined risk management and high levels of technological sophistication.
These strategies can be complex and carry significant risks, but they also provide unique opportunities for skilled traders to generate returns in various markets.
Traders interested in these strategies should start with simpler approaches and gradually build their knowledge and experience before attempting more complex techniques.