Volatility Trading


While intraday price fluctuations are common in financial markets, volatility is characterized by the swiftness and extent of these changes. Volatility trading is a strategy that involves making bets on those degrees of price fluctuations.
This guide explains how you can use various instruments and strategies to profit from either an increase or decrease in market volatility.
Quick Introduction
- Volatility trading revolves around the anticipation of price fluctuations in the market, either higher (increased volatility) or lower (decreased volatility).
- Volatility trading can be employed for both hedging and speculative purposes, facilitating the protection of portfolios or the seeking of profits during volatile periods.
- Implied volatility (expectations for future price swings) should be compared to historical volatility (past price fluctuations) to make informed decisions.
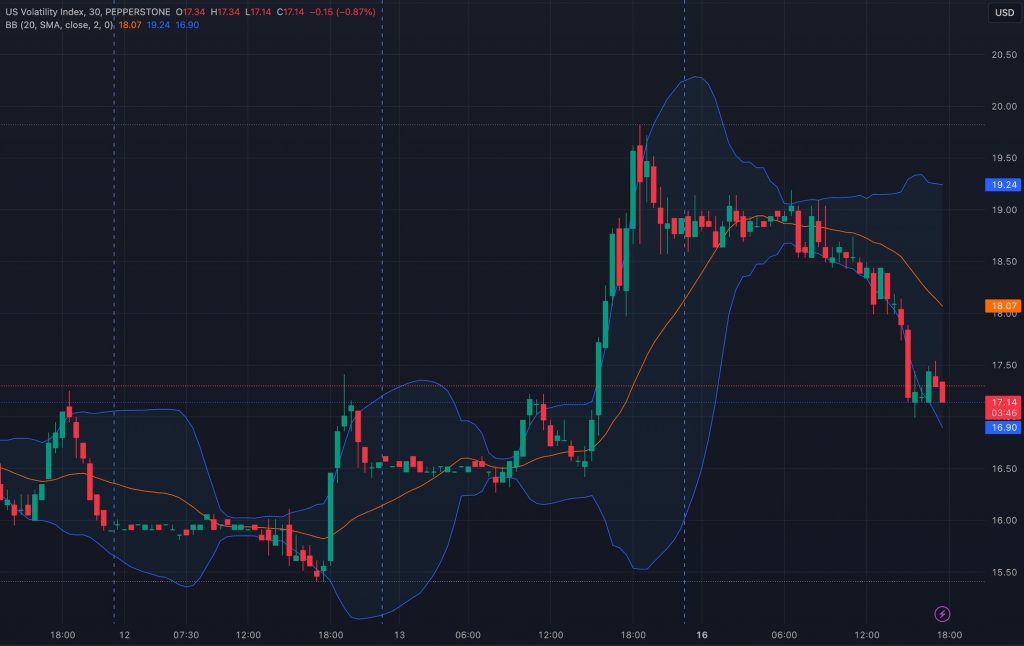
- The Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE) VIX is an important volatility index, measuring anticipated volatility in the U.S. stock market.
- Risk management is critical in volatility trading, given the potential for large price swings.
Best Volatility Trading Brokers
Based on our assessment, these are the 4 best brokers for volatility trading:
All Brokers with Volatility Index
Understanding Volatility Trading
Once understood fully, volatility trading is highly adaptable to various market conditions. It can be profitable in both bullish and bearish markets, making it versatile and enabling you to capitalize on market dynamics regardless of price direction.
This adaptability is particularly valuable in today’s ever-changing financial landscape, where market conditions can shift rapidly.
Moreover, volatility trading serves as an effective tool for diversification and risk management. It allows you to hedge your portfolios during periods of uncertainty and market stress.
By incorporating volatility-based instruments such as options or volatility ETFs, you can protect your investments and reduce exposure to potential losses, ultimately improving risk-adjusted returns.
Another key advantage of volatility trading is its potential for profit during market turbulence. Volatile conditions often coincide with significant events or economic uncertainties. You can harness this increased turbulence to generate income through options strategies or by trading the VIX, a popular gauge of market volatility.
VIX Volatility Index
The VIX (Volatility Index) is an important financial instrument often referred to as the ‘fear gauge’ or ‘fear index.’ It is designed to measure the expected volatility in the U.S. stock market, particularly within the S&P 500 Index, over the next 30 days.
Created by the Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE), the VIX derives its value from the prices of options on the S&P 500. As such, it provides insight into market sentiment and the anticipated level of price fluctuations.
The VIX is an indispensable tool for several reasons. First and foremost, it serves as a valuable indicator of market risk and uncertainty. Traders use the VIX to assess the degree of fear or complacency in the market.
A rising VIX often signifies increased market volatility and a heightened level of concern among traders, which can be a signal for potential market declines. Conversely, a declining VIX suggests reduced expected volatility and a more stable market environment.
You can use the VIX as a decision-making tool to gauge market sentiment and make informed trading choices, in addition to VIX-related products such as futures and options, to speculate on market volatility or to hedge your positions.
What Causes Market Volatility?
Volatility in financial markets can be triggered by a multitude of factors, and it’s essential that you understand these causes to navigate and respond effectively. Some of the most popular causes of volatility include:
Economic Data Releases
Economic indicators, such as GDP reports, employment data, inflation figures, and central bank decisions, can significantly impact market sentiment and trigger price swings.
Unanticipated changes in these data points can create volatility as they influence expectations about the economy.
Geopolitical Events
Geopolitical tensions, conflicts, elections, and policy decisions can have a profound impact on market stability.
Unforeseen political developments or international conflicts can lead to uncertainty, causing traders to react by buying or selling assets.
Corporate Earnings Reports
Earnings announcements from publicly traded companies can lead to considerable volatility in the stock market.
Positive or negative surprises in earnings or revenue figures often result in sharp price movements, affecting both individual stocks and broader indices.
Interest Rate Changes
Central bank decisions on interest rates, particularly from major central banks like the Federal Reserve, can have far-reaching effects.
Interest rate hikes or cuts can influence borrowing costs, consumer spending, and investment, impacting various financial markets.
Market Sentiment And Speculation
Perceptions of market conditions and future expectations can be a significant driver of volatility.
Speculative trading, investor sentiment, and behavioral biases can lead to rapid price changes, especially in assets like cryptocurrencies and meme stocks.
Liquidity Shocks
Sudden disruptions in market liquidity, such as flash crashes or large-scale selling or buying, can exacerbate volatility.
These shocks can stem from technical glitches, algorithmic trading, or other factors that disrupt market flow.
Natural Disasters And Environmental Factors
Catastrophic events like earthquakes or hurricanes can have ripple effects on financial markets.
They can disrupt supply chains, affect production, and alter investor sentiment.
Currency Movements
Foreign exchange markets can experience significant volatility due to shifts in exchange rates.
Factors such as political events, economic performance, and interest rate differentials can cause currency volatility.
Commodity Price Swings
Commodities, including oil, gold, and agricultural products, are sensitive to supply and demand dynamics, weather conditions, and geopolitical factors.
Price fluctuations in these commodities can have cascading effects on related industries and markets.
Market Structure And Algorithmic Trading
The rise of high-frequency trading and automated trading strategies can amplify market movements.
These strategies can react swiftly to market events, leading to rapid price fluctuations.
The Most Volatile Markets
The financial markets offer a wide range of instruments and asset classes to trade, and the level of volatility can vary significantly across them.
Volatility is also a relative concept, where price fluctuations perceived as highly volatile in one asset class may appear comparatively mild in another.
Some of the most volatile markets you can trade are:
Cryptocurrencies
Cryptocurrencies are one of the most volatile markets to trade due to several factors. Firstly, their relatively small market capitalization compared to traditional assets makes them more susceptible to price swings driven by supply and demand imbalances. Secondly, the lack of regulatory oversight, coupled with speculative trading, can result in abrupt price movements.
Additionally, the nascent and rapidly evolving nature of the cryptocurrency space, along with sensitivity to news and sentiment, contributes to their heightened volatility.
Traders are drawn to cryptocurrencies for the profit potential stemming from this volatility, but it also entails increased risk.
Commodities
Certain commodities, like oil, gold, and silver, are also volatile to trade for several reasons. Firstly, they are heavily influenced by supply and demand dynamics, which can be subject to rapid changes due to factors like weather conditions, geopolitical events, and production disruptions.
Commodities are often sensitive to currency fluctuations, making them vulnerable to exchange rate movements. Speculation, leveraged trading, and commodity-linked financial products can also amplify price swings, contributing to their overall volatility.
Penny Stocks
Low-priced, small-cap stocks, often referred to as penny stocks, are extremely volatile to trade primarily due to their low market capitalization and limited liquidity.
These stocks typically represent small companies with limited public information, making them susceptible to price swings driven by speculative trading, market sentiment, and news releases.
Forex
Finally, the foreign exchange market, or forex, can be highly volatile, particularly during major economic events and geopolitical developments.
In particular, exotic currency pairs involving currencies from emerging or smaller economies can experience rapid and significant price movements due to economic, political, or geopolitical events.
These currencies often lack the liquidity and stability of major currencies, making them more sensitive to external factors. Additionally, exotic pairs have wider bid-ask spreads, making it easier for prices to jump, contributing to their overall volatility.
If you plan to trade exotic currency pairs, be prepared for heightened risk and carefully manage your positions.
The Least Volatile Markets
The least volatile markets to trade are typically those with more stable and established assets or instruments, often characterized by lower price fluctuations.
These should be considered if you are seeking a more predictable and less risky trading environment.
Some of the least volatile markets you can trade are:
Stocks
Blue-chip stocks are less volatile to trade primarily due to their association with large, well-established companies with solid track records.
These companies typically have diverse revenue streams, financial stability, and established market positions, which reduce the likelihood of sudden and extreme price fluctuations.
Blue-chip stocks also tend to be less influenced by short-term market sentiment or speculative trading, contributing to their lower volatility and making them a preferred choice if you are seeking more stability and consistency in your portfolios.
Indices
Stock indices like the S&P 500, Dow Jones Industrial Average, and Nasdaq can be less volatile to trade compared to individual stocks primarily because they represent a diversified basket of multiple large-cap companies.
Any extreme price movements in individual stocks within the index tend to be balanced out by more stable or opposing movements in other constituent stocks.
This diversification reduces the overall volatility of the index and makes it less susceptible to the impact of specific company news or events, offering a more stable trading experience.
Stock indices are heavily traded for this reduced volatility and the ability to gain exposure to a broad market segment without the same level of risk associated with trading individual stocks.
Bonds
Government bonds are less volatile to trade due to their association with stable and creditworthy governments. The reliability of these governments makes their bonds relatively low-risk, as they are less likely to default on interest or principal payments.
Furthermore, government bonds are influenced by interest rate changes, which tend to be managed carefully by central banks, contributing to their overall stability and making them a favored choice for risk-averse investors seeking a consistent income stream with limited price fluctuations.
How Market Volatility Is Measured
Volatility is typically measured using various financial instruments and indicators, with the most common methods being volatility indexes (calculated based on options prices and providing a numerical representation of expected volatility over a specific timeframe), historical volatility (measures the past price movements of a financial asset) and implied volatility (derived from options prices, it represents the market’s expectation of future volatility).
Popular technical analysis tools include Average True Range (quantifies the average price range or volatility of an asset over a specified period), Bollinger Bands (uses standard deviations of price movements to determine market volatility), and Volume (high trading volumes are often associated with significant price movements and can be a real-time indicator of market sentiment).
Two other widely used measurements include Standard Deviation (a statistical measure of the dispersion or spread of data points to assess the variability of returns), and Economic Event Analysis (volatility can be inferred from significant economic events, news releases, and geopolitical developments).
An Example Volatility Trade
Making a volatility trade in gold often involves using options, which allow you to benefit from gold price swings while managing risk. Here’s an example of how to execute a volatility trade in gold using options:
Scenario
You anticipate significant volatility in the price of gold in the near future and wish to profit from potential price movements.
Step 1: Choose An Options Strategy
Select an options strategy that aligns with your market outlook. In a volatile gold market, a popular strategy is a ‘straddle.’
This system entails purchasing both a call option (betting on an increase in gold prices) and a put option (betting on a decrease in gold prices) with the same strike price and expiration date. The straddle strategy profits from substantial price swings, regardless of their direction.
Step 2: Execute The Trade
Assuming the current price of gold is $1,800 per ounce and you expect significant volatility but aren’t sure about the price direction, you decide to execute a straddle trade:
- Buy a call option: Purchase a call option with a strike price of $1,800 and an expiration date two months from today for $50 per ounce.
- Buy a put option: Also buy a put option with the same $1,800 strike price and the same two-month expiration date for $50 per ounce.
Your total cost for this straddle strategy is $100 per ounce (the combined cost of the call and put options).
Step 3: Monitor And Manage
You now have a straddle position in gold, which profits if the price of gold makes a substantial move in either direction. If gold’s price increases, your call option becomes profitable, offsetting the loss on the put option, and vice versa.
- If the price of gold rises to $1,900 per ounce, your call option could be worth $100 per ounce, resulting in a $50 profit.
- If the price of gold falls to $1,700 per ounce, your put option could be worth $100 per ounce, also resulting in a $50 profit.
Step 4: Close The Trade
Continuously monitor your options position and consider closing the trade when you’ve achieved your profit target or when you believe further price movement is unlikely. This helps you secure profits or limit potential losses.
Pros & Cons Of Volatility Trading
Pros
- Short-term and long-term opportunities: Volatility trading works well with both short-term and long-term strategies, including scalping and swing trading.
- Volatility risk premium: When trading options, you can benefit from what’s known as a risk premium, which is the compensation that you earn for protecting yourself against losses. There are numerous research papers online that explain the behavioural bias towards risk and loss.
- Circuit breaker halts: If a stock suddenly moves up or down too quickly within a 5-minute period, it can cause an automatic circuit breaker halt that will pause trading temporarily. This can happen in anticipation of a major news announcement and can be a huge opportunity to profit if the asset reopens higher.
- Benefits of options: Options are a great way to diversify your portfolio. They also have low capital requirements and allow you to trade on leverage.
- Profit potential: Volatility is a key metric of profit potential and can come with big rewards if risk management tools have been applied appropriately.
Cons
- Requires patience and resilience: Trading volatility can be stressful and anxiety-inducing for beginners or unprepared traders. It’s worth carrying out some virtual trades within a demo platform before committing
- Limitations of options: The options market offers lower liquidity and trading volume and therefore higher spreads, compared to other markets.
- Circuit breaker halts: Some trading pauses have been known to go on for hours or sometimes even days. If you’re stuck in a halt for a longer period of time, this can cause anxiety, especially if the price reopens lower. Note that different assets may have different circuit breaker rules.
- Risk to funds: As with all trading, high volatility comes with greater risk because the market can move erratically and unpredictably.
- Leverage risk: Trading on margin can boost your gains but it can also amplify losses if not used correctly. You should always employ stop-loss and exit strategies.
Bottom Line
Whether you’re a novice just beginning your trading journey or a seasoned expert with considerable experience, considering volatility trading as a complementary strategy in your portfolio could be a wise move. Nevertheless, it’s imperative to carefully assess the associated risks before proceeding.
Additionally, the strategies outlined in this guide may not suit every individual and do not guarantee sustained success. With the appropriate knowledge and mindset, you can tailor a volatility trading plan that suits your needs.
It’s advisable to practice and refine your strategy within a risk-free demo account before implementing it in the live market.
FAQ
What Is Volatility Trading?
Volatility trading is a strategy that aims to profit from price fluctuations in financial assets, like stocks or currencies.
It involves using options, derivatives, or other instruments to take advantage of market uncertainty and can be both rewarding and risky, so traders should approach it with caution and a solid understanding of the associated risks.
Is Volatility Trading Suitable For Beginners?
Volatility trading is generally not suitable for beginners due to its complexity and higher risk level.
New traders are better served by starting with simpler strategies and gaining experience before exploring more advanced techniques like volatility trading.
Is Volatility Trading Profitable?
Volatility trading can be profitable when executed effectively, but it also carries significant risks. Success in volatility trading requires a strong understanding of market dynamics, risk management, and the ability to adapt to changing conditions.
Can You Trade The VIX?
You can trade the VIX, also known as the CBOE Volatility Index, through various financial instruments such as VIX futures, options, and exchange-traded funds (ETFs).
However, it’s essential to have a good understanding of volatility products and associated risks, as trading the VIX can be complex and highly speculative.
Recommended Reading
Article Sources
- CBOE - Volatility Index Products
- Volatility Trading, Euan Sinclair, 2011
- Trading Volatility: Trading Volatility, Correlation, Term Structure and Skew, Colin Bennett, 2014
The writing and editorial team at DayTrading.com use credible sources to support their work. These include government agencies, white papers, research institutes, and engagement with industry professionals. Content is written free from bias and is fact-checked where appropriate. Learn more about why you can trust DayTrading.com



