Swing Trading



Swing trading is one of the most popular strategies, offering traders the opportunity to capitalize on short to medium-term price fluctuations in market trends.
This tutorial explains how to swing trade for beginners, from the basics to risk management and tips for success.
Quick Introduction
- A swing trader seeks to capture gains by holding an instrument anywhere from overnight to several weeks.
- The primary objective is to profit from price oscillations or ‘swings’ that occur as assets fluctuate between support and resistance levels or within well-defined technical patterns.
- You can swing trade in popular financial markets, including stocks, forex and commodities.
Top Swing Trading Brokers
Our experts found that these 4 brokers offer the best accounts, fees and tools for swing traders:
Download our free Swing Trading PDF Guide.
What Is Swing Trading?
Swing trading is primarily focused on capturing short to medium-term price movements within an underlying asset, such as stocks, commodities, forex or cryptocurrencies.
Unlike day trading, which involves rapid buying and selling within the same trading session, when swing trading you typically hold positions for several days to weeks.
Swing traders employ a combination of technical and fundamental analysis to identify potential entry and exit points, with a keen focus on risk management.
This type of trading aims to capitalize on market inefficiencies, news-driven events, or shifts in sentiment that can lead to price reversals or trends. By carefully timing your trades and adhering to predefined risk-reward ratios, you can achieve consistent profitability while mitigating the inherent risks associated with trading in volatile financial markets.
Swing Trading vs Day Trading
Swing trading and day trading are both active trading strategies, but they differ significantly in terms of their time horizons and trading styles:
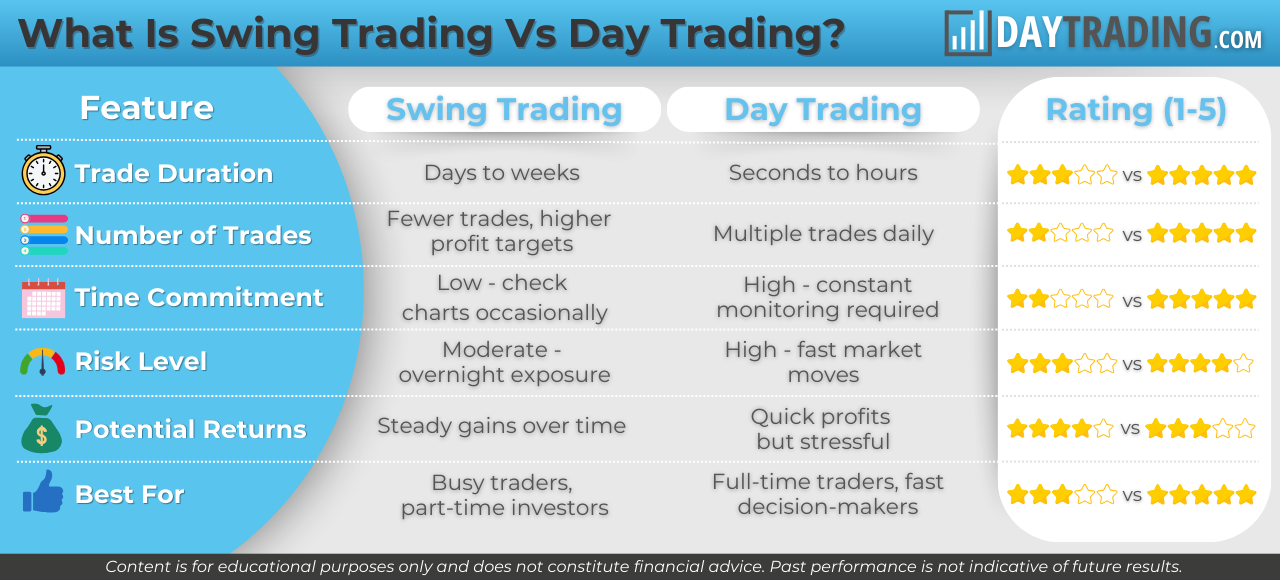
Pros & Cons
Pros
- Diversification: Swing trading allows you to hold multiple positions simultaneously, diversifying your portfolio across different assets and sectors. This diversification can help spread risk and reduce the impact of adverse price movements in any single asset, potentially enhancing overall portfolio stability.
- Potential For Large Profits: Swing trading aims to capture medium-term trends, which can lead to larger profit opportunities compared to day trading.
- Reduced Stress: Swing trading allows for a less frantic pace compared to day trading, reducing stress and emotional pressure.
- More Flexibility: You have more time for analysis, making swing trading suitable for part-time or full-time traders.
- Lower Transaction Costs: Fewer trades mean lower transaction costs in terms of commissions and spreads.
Cons
- Overnight Risks: Holding positions overnight exposes you to overnight risk, including potential gaps in prices.
- Trend Dependency: Swing trading relies heavily on identifying and riding trends, which may not always be present in all markets.
- Margin Requirements: Depending on your broker and strategy, swing trading may require significant capital to meet margin requirements for multiple positions.
- Limited Frequency: Fewer trading opportunities may be available compared to day trading, potentially leading to slower portfolio growth.
- Lack Of Immediate Feedback: You will need to wait longer to see the results of your trades, which can make it harder to adjust strategies.
How To Swing Trade
Here is an example of how to make a swing trade. However, note that this example is simplified for illustration purposes.
Market Analysis
Begin by analyzing the market to identify a potential swing trade opportunity. Let’s say you’re interested in swing trading a stock. You perform technical analysis and notice that Company XYZ has been in a strong uptrend for several weeks, and it’s currently trading near a well-defined support level. This support level indicates a potential entry point for a swing trade.
Entry Point
You decide to enter the trade if the stock’s price dips to the support level, which is at $50 per share. You set a buy limit order at $50, which means your order will only execute if the stock’s price reaches or goes below $50.
Risk Management
To manage risk, you set a stop-loss order at $48. This means that if the stock’s price drops to $48, your stop-loss order will automatically sell your shares to limit potential losses.
Position Sizing
Determining the size of your position based on your risk tolerance and account size is critical. Let’s say you decide to risk no more than 2% of your total trading capital on this trade. If your trading capital is $10,000, your maximum risk for this trade would be $200.
Trade Execution
The stock’s price reaches your entry point at $50, and your buy limit order is executed. You now hold a long position in Company XYZ.
Monitor The Trade
As a swing trader, you intend to hold the position for several days to weeks. During this time, you closely monitor the stock’s price and overall market conditions.
Exit Strategy
You have two potential exit strategies:
- If the stock’s price rises to your desired profit target, let’s say $60, you can place a sell limit order (take profit) at $60 to take your profits.
- If the stock’s price falls and hits your stop-loss at $48, your position is automatically sold to limit your losses.
Evaluate and Learn
After the trade is complete, review your trade journal and assess your performance. Analyze what worked well and what didn’t, and use this information to refine your swing trading strategy for future trades.
10 Tips For Swing Trading
Successful swing trading requires a well-defined strategy and a disciplined approach. While there’s no one-size-fits-all answer, here are the key elements that can contribute to a successful swing trading strategy:
1. Technical Analysis
Utilize technical indicators and chart patterns to identify potential entry and exit points. Look for clear trends, support and resistance levels, moving averages, and other technical signals to guide your trades.
2. Fundamental Analysis
Incorporate fundamental analysis to select assets with strong growth potential or undervalued securities. This can include examining financial reports, news, and economic factors that might impact your chosen assets.
3. Risk Management
Implement effective risk management techniques to protect your capital. Set stop-loss orders to limit potential losses, and determine your risk-reward ratio for each trade to ensure that potential gains outweigh potential losses.
4. Position Sizing
Carefully determine the size of each position based on your risk tolerance and account size. Avoid over-leveraging, as it can lead to significant losses.
5. Time Frame Selection
Define the duration of your swing trades. Swing trading typically involves holding positions for days to weeks, so choose a time frame that aligns with your strategy and market analysis.
6. Entry And Exit Rules
Establish clear criteria for entering and exiting trades. This might include specific price levels, technical indicator signals, or fundamental triggers.
7. Backtesting
Test your strategy on historical data to assess its effectiveness and refine it as needed. This can help identify strengths and weaknesses in your approach.
8. Discipline
Maintain discipline and emotional control. Avoid chasing the market or deviating from your plan due to fear or greed. Stick to your strategy, even if some trades result in losses.
9. Portfolio Diversification
Avoid putting all your capital into a single trade. Diversify your portfolio to spread risk across different assets or sectors.
10. Record-Keeping
Maintain a trading journal to track your trades, outcomes, and lessons learned. This can help you identify patterns in your trading behavior and make necessary adjustments.
Bottom Line
Swing trading offers a balanced approach to trading, providing more flexibility and reduced stress compared to day trading, while still offering the potential for significant profits. It allows you to take advantage of short-term market inefficiencies, news-driven events, or shifts in market sentiment, all while implementing effective risk management strategies such as stop-loss orders and position sizing.
Successful swing trading requires discipline, continuous learning, and the ability to adapt to changing market conditions, making it a popular choice for traders looking to achieve returns in volatile financial markets.
Importantly, no strategy guarantees success, and losses are an inherent part of online trading. It is essential to have realistic expectations and be prepared for both winning and losing trades.
FAQ
Is Swing Trading Suitable For Beginners?
Swing trading can be challenging for beginners due to its active and speculative nature. It requires a good understanding of technical and fundamental analysis, risk management, and emotional discipline.
Is Swing Trading The Same As Investing?
No. Swing trading is a short to medium-term trading strategy that aims to profit from price fluctuations within a defined timeframe, typically days to weeks. It involves actively buying and selling assets to capitalize on market volatility.
Investing, on the other hand, is a long-term strategy focused on buying and holding assets with the expectation of long-term growth and income generation, often spanning years or even decades. While both involve financial markets, swing trading is more speculative and involves frequent trading, while investing is typically characterized by a buy-and-hold approach.
Is Swing Trading Better Than Day Trading?
Whether swing trading is better than day trading depends on your preferences, risk tolerance, and trading goals. Swing trading offers a less stressful and more flexible approach, making it suitable for traders with limited time and a preference for short to medium-term positions.
Day trading, on the other hand, demands intense focus and quick decision-making but offers the potential for daily income. The choice between the two should align with your personality and trading style. There is no universally superior approach, as both have their merits and drawbacks.
What Timeframe Is Best For Swing Trading?
The best timeframe for swing trading typically falls within the daily (D1) and weekly (W1) timeframes. These longer timeframes allow you to capture short to medium-term price movements while avoiding excessive market noise seen in shorter intraday timeframes.
However, the specific timeframe can vary depending on your strategy, goals, and asset being traded. It is important to select a timeframe that aligns with your trading style and provides clear and reliable technical signals for your chosen assets.
Can You Only Swing Trade Stocks?
Swing trading can be applied to a wide range of financial assets, including stocks, forex (currency pairs), commodities (raw materials or primary agricultural products), cryptocurrencies (assets like Bitcoin and Ethereum), Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs), options and futures.
The choice of asset depends on your trading strategy, risk tolerance, and market knowledge, as each asset class comes with its unique characteristics and considerations.
How Much Money Do You Need To Swing Trade?
The amount of money you need to swing trade depends on various factors, including your risk tolerance, chosen assets, and trading strategy. While you can start swing trading with a relatively modest amount of capital, having sufficient funds is essential to diversify your positions, manage risk effectively, and cover potential losses.
It is generally recommended to have a trading account with enough capital to risk no more than 1-2% of your total trading capital on any single trade, as this helps protect your account from significant drawdowns.
Does Swing Trading Really Work?
Swing trading can work successfully when executed with a well-researched and disciplined approach. However, its effectiveness depends on various factors, including market conditions, your trading skills and experience, and your risk management. While some traders achieve consistent profits with swing trading, others may face losses.
It is important to thoroughly educate yourself, practice, and develop a robust strategy to increase the likelihood of success in swing trading.
Recommended Reading
Article Sources
- Swing Trading: Power Strategies to Cut Risk and Boost Profits, Jon D. Markman
- Swing Trading For Dummies, Omar Bassal
- Swing Trading: The Definitive And Step by Step Guide To Swing Trading, Andrew Johnson
- Mastering The Trade, John F Carter
- Come Into My Trading Room, Dr Alexander Elder
- Trade Your Way To Financial Freedom, Dr Van K Tharp
The writing and editorial team at DayTrading.com use credible sources to support their work. These include government agencies, white papers, research institutes, and engagement with industry professionals. Content is written free from bias and is fact-checked where appropriate. Learn more about why you can trust DayTrading.com



