Dividend Income Investing Guide

Dividend income from stocks offers an attractive way to earn passive revenue while building a diverse portfolio. But what is dividend income and how can you get started dividend investing? In this guide, we look at the types of stocks with the highest dividend yields, key metrics and definitions to aid investment decisions, coverage ratios and more. We also consider the taxability of dividend income, looking at whether returns are taxable and common rates of tax in 2025.
Use our list of brokers that offer the best dividend stocks to start investing today.
Top Stock Brokers
What Is Dividend Income?
Dividend income is the distribution of a domestic or international company’s or corporation’s earnings to its shareholders in the form of cash dividends. Dividends are typically paid out quarterly, but some companies estimate and pay them out more or less frequently.
Dividend payments are usually made to shareholders who own the stock on the dividend record date, which is usually two days before the dividend payment date. The dividend yield is the percentage of a company’s share price that is paid out in dividends. For example, if a company has a dividend yield of 3 percent, that means it pays out $3 in dividends for every $100 of stock price.
The dividend coverage ratio is a measure of a company’s ability to pay its dividend. It is calculated by dividing the company’s cash flow or cash flow proxy such as its earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) by its dividend payments. A coverage ratio of 1.5 or higher is considered healthy.
Dividend Investing
Dividend investing is the generalized process of buying shares in dividend-paying companies to receive dynamic dividend income. Dividend investing can be a great way to earn passive income and build an enhanced, diversified investment portfolio.
When choosing dividend stocks and funds, it is important to consider a company’s dividend history, as well as its current dividend yield and its ability to cover that payment with the earnings of the business. A company’s dividend history can give you insight into its financial stability and dividend-paying ability. A company’s current dividend yield is a good indicator of its current dividend payments.
Pros Of Investing In Dividend Stocks
Dividend stocks offer several benefits:
- A source of regular income – Dividend stocks can provide you with a source of regular income that can help you meet your financial goals. For example, once you’re making $3,000 per month in income from your investments that can about cover your monthly living expenses if you live a fairly modest lifestyle.
- Potential for capital appreciation – While dividend payments are typically rather small, over time they can add up. Additionally, as the company’s stock price increases, so does the value of your dividend payments.
- A hedge against inflation – Dividend payments tend to increase over time, which can help offset the effects of inflation. A well-diversified dividend portfolio can also approximate total spending in an economy, which should roughly net out to nominal growth, which is real growth plus inflation.
- A way to diversify your portfolio – Dividend shares can help you diversify your portfolio and reduce your overall risk.
Receiving Dividends
If you own shares in a company that pays dividends, you will receive dividend payments based on the number of shares you own.
For example, if you own 100 shares of ABC Company and ABC Company pays a dividend of $1 per share, you will receive $100 in dividend income.
Dividend Calendars Explained
A dividend calendar is a schedule of when companies are expected to announce and pay out their dividend payments. This information is important for dividend investors, as it allows them to plan for when they will receive upcoming dividend income.
The dividend calendar can be found on most financial websites, including Yahoo Finance and Morningstar.
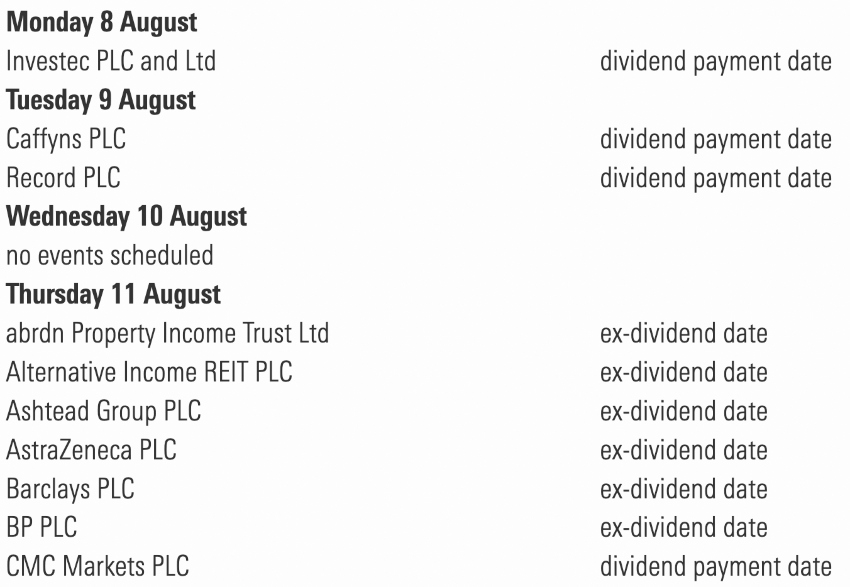
Dividend Timings
Dividends are most commonly paid quarter, or four times per year. However, there are some stocks that pay monthly dividend income.
Some investors also choose to stagger their dividend investments such that they receive roughly equal allotments of dividend income each month. This is called dividend laddering. That way they can match up better with their monthly payments, since most bills are due on a monthly timeframe despite dividend income coming in quarterly. (Bonds often pay only semi-annually, or every six months.)
Some companies issue dividends January, April, July, and October. Others do February, May, August, and November. Others do March, June, September, and December.
The first group is often the most common since they often pay out after closing a quarter. But it varies. By combining the three groups, you can spreads thing out more equally. Nonetheless, what’s most important is the quality of the investment, not when it pays out.
Important Dividend Dates
Ex-Dividend Date
The ex-dividend date is the date on which a dividend-paying equity goes “ex-dividend”. This means that the stock no longer comes with the right to receive the dividend payment. If you want to receive the dividend, you must own the stock before the ex-dividend date.
The ex-dividend date is commonly two business days or so before the dividend is paid. For example, if a company declared a dividend payable on December 15, the ex-dividend date might be December 11. This is because the dividend will be paid to shareholders of record as of December 12. If you buy the stock on December 11, you will not receive the dividend, the seller of the stock will receive it. However, if you buy the stock on December 10, you will receive the dividend.
Record Date
The record date is the date on which a dividend-paying company’s shares must be held in order to receive the dividend payment. For example, if a company declared a dividend payable on December 15, the record date would be December 12. This is because the dividend will be paid to shareholders of record as of December 12.
If you own the stocks on December 12, you will receive the dividend. If you sell the stocks on December 12, you will not receive the dividend.
Dividend Payment Date
The dividend payment date is the date on which the dividend is actually paid to shareholders. For example, if a company declared a dividend payable on December 15, the dividend payment date would be December 15. This is the date on which the dividend will be paid to shareholders of record as of December 12. If you own the stock on December 12, you will receive the dividend on December 15.
Benefits Of Dividend Income
Dividend income can provide a steady stream of passive income. Unlike interest from a savings account or bonds, dividend payments are not guaranteed. However, over time, dividend payments have averaged around 3-4 percent of the stock market’s overall return.
Dividend income can also help to diversify your investment portfolio. By owning shares in dividend-paying companies, you can reduce your overall risk while still earning a return on your investment.
Risks Of Dividend Income
The biggest drawback of dividend income is that it is not guaranteed. Dividend payments can fluctuate based on a company’s profitability and may be cut or eliminated altogether if a company is struggling financially.
Another downside of dividend income is that in many jurisdictions it is taxed as ordinary income, which means it is subject to a higher tax rate than other types of investment income, such as capital gains.
Stocks can also move in price significantly. For example, if a company offers a 3 percent annual dividend yield, it’s very easy for that amount to be wiped out in a day when the stock performs poorly. This is why diversification is important and adopting a longer-term mindset.
How To Calculate Dividend Income
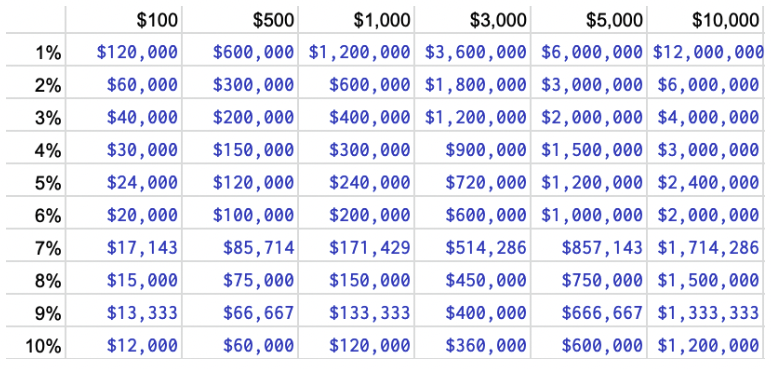
Your dividend income is a function of how much you have invested and the dividend yield. For example, if your portfolio has an average yield of 5 percent with $100,000 invested, you can expect to get $5,000 in dividend income per year.
Below is a table showing monthly dividend income on the top and yield on the left and how much needs to be invested to reach those monthly dividend amounts accordingly.
Common Types Of Dividend Stocks
REITs
A REIT, or real estate investment trust, is a type of investment that allows you to invest in the ownership and operation of real estate properties. REITs can be a great way to earn dividend income, as many REITs are required by law to pay out at least 90 percent of their earnings to shareholders in the form of dividends.
There are two main types of REITs:
- Equity REITs – Equity REITs own and operate income-producing real estate properties, such as office buildings, shopping centers, and apartments.
- Mortgage REITs – Mortgage REITs provide financing for income-producing real estate properties through mortgages and other loans.
BDCs
A business development company, or BDC, is a type of investment company that invests in small and mid-sized businesses. BDCs are required by law to pay out at least 90 percent of their earnings to shareholders in the form of dividends.
BDCs can be a great way to earn dividend income from setups similar to stocks, and can typically have high dividend yields. However, BDCs are also high-risk investments, as they are subject to the same risks as the businesses they invest in. As a result, they tend to have higher volatility as they are largely subprime lenders.
MLPs
A master limited partnership, or MLP, is a type of partnership that is publicly traded on a stock exchange. MLPs are often used by energy and natural resources companies to raise capital. MLPs are required by law to pay out at least 90 percent of their earnings to shareholders in the form of dividends.
MLPs can be a great way to earn dividend income, but they are also high-risk investments.
Common Stock
Lots of otherwise regular stocks pay out dividends. When you buy shares of common stock, you become a part-owner of the company. Common stockholders have voting rights and can elect the company’s board of directors.
Dividend payments on common stock are not guaranteed, but many companies do pay dividends to their shareholders. Dividends on common stock are typically paid quarterly.
Preferred Stock
Preferred stock is a type of stock that gives shareholders preference over common stockholders in the event of a liquidation. Preferred stockholders also typically receive dividend payments before common stockholders. Dividends on preferred stock are typically paid quarterly, but they may be paid more or less often, depending on the company.
ETFs
Many exchange-traded funds, or ETFs, provide dividends, including popular indices like SPY. There are dividend-focused ETFs and mutual funds as well. However, they tend to have higher fees.
Dividend Finance
Dividend finance is the process of using dividend income to help finance your investment portfolio. Dividend finance can be a great way to build a diversified investment portfolio without having to use all of your own money.
When dividend investing, it is important to consider dividend financing options. One option is to use dividend reinvestment plans, or DRIPs. DRIPs allow you to reinvest your dividend payments back into the company’s stock, allowing you to buy additional shares over time.
Another option for dividend financing is to use a dividend exchange-traded fund, or ETF. A dividend ETF allows you to invest in a basket of dividend-paying stocks, providing you with exposure to a variety of companies.
Coverage Ratio Explained
The coverage ratio is one of the most important financial metrics when it comes to dividend investing. This pertains to the dividend payout ratio, which is the percentage of a company’s earnings that is paid out in dividends.
Payout ratio = Dividends per share ÷ Earnings per share (EPS)
The coverage ratio is a similar metric, but it looks at the percentage of a company’s cash flow that is paid out in dividends.
The cash flow coverage ratio is a more accurate metric to use when dividend investing because it takes into account a company’s capital expenditures.
A company might have high earnings but low cash flow due to its capex or working capital, which would make its dividend less sustainable. Ideally, you want to look for companies with dividend coverage ratios above 1.5. This means that the company has enough cash flow to cover its dividend payments and then some.
If a company is paying a dividend and has cash left to spare, then shareholders may enjoy some capital appreciation in the stock over the long run as well, in contrast to a company that is paying out everything and may likely have a flat stock over time.
If a company’s earnings are close to its dividend payout, it could be considered a risk. If earnings (or more accurately, operational or overall cash flow) don’t cover the dividend, a company will need to tap into its cash reserves, issue debt, issue equity, or cut the dividend.
Don’t Overemphasize Dividend Yield
There is a tendency to look at the dividend yield first, but this is not the most important factor. The dividend yield is simply the dividend per share divided by the stock price.
For example, if a company has a dividend of $1 per share and the stock price is $100, then the dividend yield would be 1 percent. If the stock price goes to $200, then the dividend yield would be 0.5 percent.
The dividend yield can go up or down depending on the stock price, but this doesn’t necessarily mean that the dividend itself is going up or down or that the stock is better or worse. A high dividend yield could be a sign that the market is bearish on the stock and expects the dividend to be cut in the future. Therefore, you should always look at the dividend coverage ratio before making any investment decisions. So you don’t want to just focus on cheap stocks with a high dividend.
And also make sure that the data you’re getting is accurate. Dividend payouts change all the time, so information on some websites (or the data displayed directly in Google search results) can be outdated. Always cross-check any information you see.
Dividend Payables
Brokers will often add a dividend payable to a customer’s account to keep an account balance steady. The dividend payable is the dividend per share multiplied by the number of shares owned. For example, if a company has a dividend of $1 per share and you own 100 shares, then the dividend payable would be $100. This dividend will be paid to you on the dividend payment date.
It is important to note that the dividend payable is not the same as cash flow. Dividends are paid out of a company’s earnings, not its cash flow. Therefore, a company can have strong cash flow but low earnings, which would make its dividend less sustainable.
Average Return On Dividend Stocks
The average dividend stock yielded 2.9 percent per the most recent data points.
What If I’m Already Retired?
If you’re already retired, you won’t have the benefit of having decades to compound returns like someone who is younger. In this case, for retired investors looking to live off their dividends and investments, they may want to increase their portfolio’s yield.
At the same time, don’t overemphasize yield. Some stocks and investments that have high dividend yields have seen their fortunes recently turn and may be likely to cut their dividends. Or the principal may be likely to erode.
For other types of investments outside stocks and bonds, we have an article on unique investments located here.
Dividend Income Tax
Taxation of dividend income varies between jurisdictions. However, dividends are normally subject to income tax. In the UK, for example, that means investors can make use of the Personal Allowance (£12,750 in 2022/2023), plus the £2,000 individual dividend allowance. After this, profits are charged in line with the relevant income tax bracket.
Annual dividend income tax calculators can also be found online for free. These estimators can help draft tax statements, taking into account your taxation allowance. It is also worth considering that taxation rules vary in different countries, from the UK and Canada to Australia, Hong Kong, Malaysia and India.
Alternatively, investors can consult a local accountant for guidance. Accountants can answer questions such as ‘do I need to pay and report tax on dividend income?’ and ‘how much dividend income is tax free?’. They can also work through accounting and journal entry requirements, deductions and relevant exemption limits, advance tax, rates for foreign dividend income (non resident), and more.
Note, corporation tax and its impact on cash flow statements and balance sheets may be treated differently. Also keep an eye on new tax rules relating to dividend income.
Final Thoughts On Dividend Income
Dividend income can be a great way to earn passive income and build a diversified investment portfolio. When choosing dividend stocks, it is important to consider a company’s dividend history and its current dividend yield. REITs, BDCs, and MLPs can be great sources of dividend income, but they are also high-risk investments. Common stock and preferred stock are two other types of dividend-paying investments.
Use our list of top-rated brokers to start investing in dividend stocks.
FAQs
What Are The Distributions Of Either Cash Or Stock To Shareholders Called?
They are called dividends.
What Is The Dividend Yield?
The dividend yield is the dividend rate divided by the current share price.
What Is Dividend Income?
Dividend income is the payments made to shareholders by companies in which they have invested. When you buy shares of stock in a company, you become a shareholder. If the company pays dividends, you will receive dividend payments based on the number of shares you own. Dividend payments are not guaranteed, but many companies do pay dividends to their shareholders as a way to give distribute cash back.
Dividends are typically paid quarterly, but they may be paid more or less often, depending on the company. Dividend income can be a great way to earn additional income on your investment portfolio. It’s nonetheless important to remember that dividend payments are not guaranteed and they can be reduced or eliminated entirely at any time by the company. Big names like Berkshire Hathaway, for example, do not pay dividend income (though Warren Buffett regularly collects a large amount in dividends).
What Factors Should I Consider Before Investing In A Company For Dividend Income?
When considering dividend stocks, there are a few key factors you should look at:
- Dividend yield – This is the dividend per share divided by the stock price. A higher dividend yield typically means a better return on your investment.
- Dividend coverage ratio – This is the percentage of a company’s cash flow that is paid out in dividends. You want to look for companies with dividend coverage ratios above 1.5, which means they have enough cash flow to cover their dividend payments and then some.
- Don’t put too much emphasis on the dividend yield itself – The dividend yield is not the most important factor when it comes to any investment. A high dividend yield could indicate that the stock recently fell because of a change in its fortunes and the dividend is likely to be cut in the future.
Always look at the dividend coverage ratio before making any investment decisions.
What Are Some Of The Risks Associated With Dividend Investing?
There are a few risks to consider when investing in dividend stocks:
- The dividend may be cut or eliminated at any time – Dividend payments are not guaranteed and can be altered by the company at any time.
- Your investment may lose value – Like all investments, there is always the risk that your investment will lose value. No matter the dividend yield, the stock can always fall by more than that.
- You may not receive your dividends – If a company gets into financial trouble or goes bankrupt, shareholders may not receive their dividend payments.
- Dividends are taxed – Dividend payments are subject to income tax.
What Are Some Of The Benefits Of Dividend Investing?
There are a few benefits to consider when investing in dividend stocks:
- Dividend payments can provide you with a source of income – Dividend payments can provide you with extra income, which can be helpful if you are retired or otherwise hoping to live off dividends.
- Dividends can help offset share price volatility – If the stock market is volatile, dividend payments can help offset some of the losses you may experience in your investment portfolio.
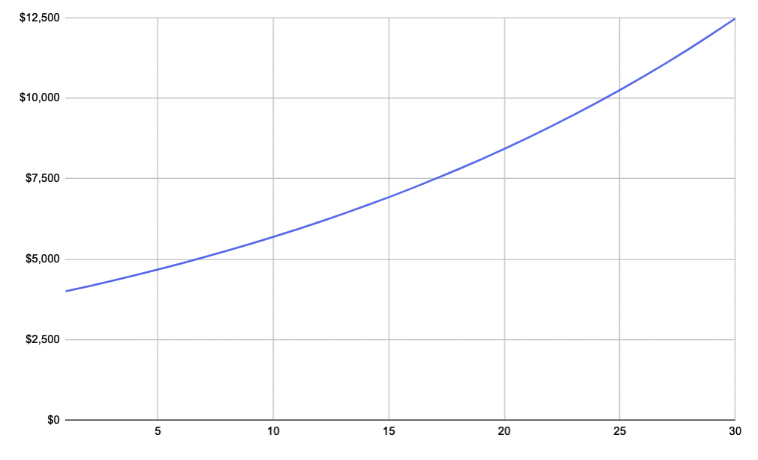
- Dividend payments can increase over time – If a company is doing well, the dividend payments may increase over time. This can provide you with a nice return on your investment. As a company’s earnings increase, so should your dividends. Moreover, just the act of reinvesting your dividends will help your portfolio and income grow. For example, let’s say you start out with $100k and invest in a stock that provides you a 4 percent dividend each year. And if you assume no capital appreciation, if you continually reinvest that dividend over 30 years, you’ll eventually have an investment that throws off about $12,500 per year, or about 12.5 percent of your original investment.
- Dividends can be reinvested – Many companies offer dividend reinvestment plans, which allow you to use your dividend payments to purchase additional shares of stock in the company. This can help you grow your investment over time.
What Is A Good Dividend Yield?
There is no one-size-fits-all answer to this question. A good dividend yield will depend on your investment goals and objectives. Generally, a dividend yield of 3 percent or higher is considered to be a good dividend yield.
Particularly popular firms, stocks and funds that provide dividend income include Columbia, BMO, CIBC, Fidelity, Franklin, Europac, Invesco, and Madison. You can do an average dividend income yield lookup online for the respective fund. You can also try Google for a list of the best best international mutual funds for monthly dividend income. Your online broker may also provide watchlists.
What Is A Good Dividend Coverage Ratio?
As a general rule of thumb, you want to look for companies with dividend coverage ratios above 1.5. This means that the company has enough cash flow to cover its dividend payments and then some.
What Are Some Of The Best Dividend Stocks?
There are many great dividend stocks out there. We won’t give outright recommendations, but we encourage looking at lists like the Dividend Aristocrats, Dividend Kings, and Dividend Champions. These are lists of companies that have increased their dividend payout for several years in a row and are considered some of the best dividend stocks.
Do All Stocks Pay Dividends?
No, not all stocks pay dividends. Many companies choose to reinvest their profits back into the business rather than paying out dividends to shareholders.
Why Do Companies Pay Dividends?
Companies may pay dividends for a variety of reasons. Many companies choose to pay dividends as a way to return money to shareholders. Others may do it to offset stock price volatility or as a way to attract and retain investors. When a company is relatively mature and stable, it is often the most efficient way to return money to its shareholders. For this reason, we rarely see young companies that are growing a lot issue a dividend (some issue a nominal dividend to diversify their shareholder base to some degree), but it’s common among older businesses.
What Are Dividend Reinvestment Plans?
Dividend reinvestment plans (DRIPs) are programs offered by some companies that allow you to use your dividend payments to purchase additional shares of stock in the company. This can help you grow your investment over time. Accordingly, dividends can be paid out in terms of cash or additional stock under a DRIP.
How Are Dividend Payments Taxed?
Dividend payments are subject to income tax. The exact tax rate will depend on your individual tax situation.
Do I Need To Own A Lot Of Shares To Receive Dividend Payments?
No, you don’t need to own a lot of shares to receive dividend payments. However, the more shares you own, the higher your dividend payments will be.
Why Does The Price Of A Dividend Stock Fall On The Ex-Dividend Date?
Dividends are paid out of a company’s cash balance. When a dividend yield is declared, the realty company’s cash balance, for example, falls by the amount of the dividend. This often causes the stock price and income to fall on the ex dividend date (the date on which the dividend is paid).
How Often Are Dividends Paid?
Dividends are typically paid quarterly, but some companies may pay them more or less often.
What Is A Dividend Aristocrat?
A dividend aristocrat is a company that has increased its dividend payout for at least 25 consecutive years. Dividend aristocrats are considered to be some of the best dividend stocks.
What Is A Dividend King?
A dividend king is a company that has increased its dividend payout for at least 50 consecutive years.
What Are Some Of The Downsides Of Investing In Dividend Stocks?
Dividend stocks can have drawbacks in the sense that they are more mature companies with lower yields. This means that they may not have as much room for growth as younger companies. Additionally, dividend payments can be cut if a company’s financial situation deteriorates. Finally, dividend stocks may be more volatile than safer types of investments (e.g., many forms of bonds) during market downturns.
Is Dividend Investing Worth It?
Dividend investing can be a great way to build wealth over time. However, it is not without risk. Before investing in dividend stocks, be sure to do your research and understand the risks involved.
What Are Special Dividends?
Special dividends are dividend payments that are above and beyond a company’s regular dividend payments. They are often one-time payments and are not paid on a regular basis.
What Is The Difference Between Dividends And Share Repurchases?
Dividends are payments made by a company to its shareholders out of its profits. Share repurchases are when a company buys back its own shares from shareholders. Both dividend payments and share repurchases can return cash to shareholders. However, dividend payments are typically made on a regular basis (monthly, quarterly, semi-annually, or annually), while share repurchases can be done at any time and are often not done on a regular basis.
How Can I Start Investing In Dividend Stocks?
The best way to start investing in dividend stocks is to open a brokerage account and begin buying shares of dividend stocks that interest you. Many brokerages offer commission-free trading, so you can buy and sell dividend stocks without paying any commissions. Alternatively, you can invest in dividend stock mutual funds or ETFs. These are funds that hold a basket of dividend stocks and can be purchased commission-free at some brokers as well.
What Are The Safest, Most Stable Dividend Stocks?
Generally speaking, the most stable forms of income relate to things that people always need. People always need food, basic medicine, water, electricity, and the basic staples of life. For this reason, many dividend investors seek out consumer staples and utility stocks for dividends. And it’s also for this reason that many dividend stocks are seen in these industries. And why many traders and investors consider certain dividend stocks reliable stores of value.



