Japan’s Inflation Hits 4.0%, Highest Since 2023
- This topic has 0 replies, 1 voice, and was last updated 1 month ago by .
-
Topic
-
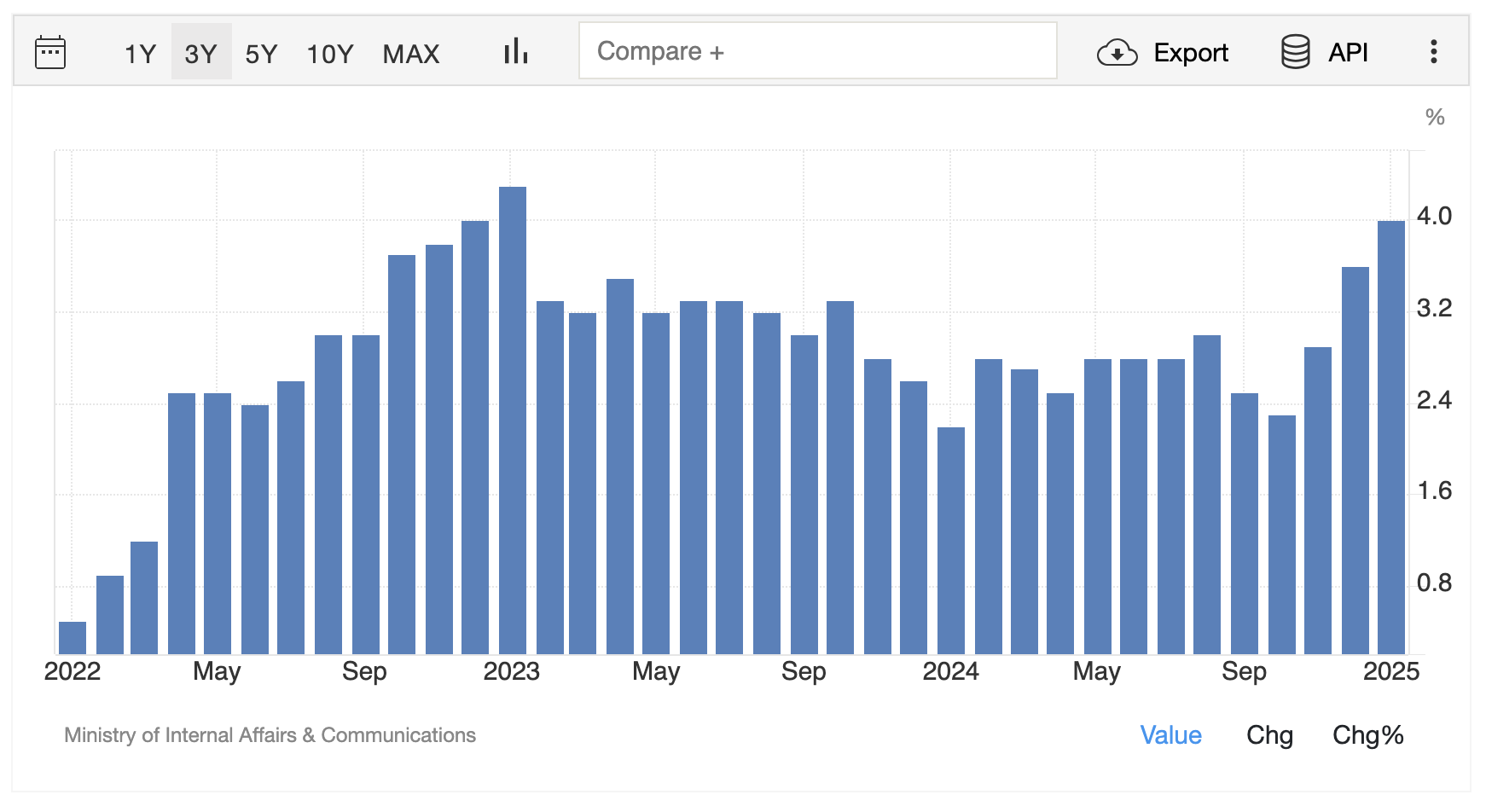
Japan’s annual inflation rate surged to 4.0% in January 2025, up from 3.6% in December, reaching its highest level since January 2023.
This increase was primarily driven by a sharp rise in food prices, which climbed at the fastest rate in 15 months, with fresh vegetables and other fresh food items leading the upturn.
The core inflation rate, which excludes fresh food prices, rose to 3.2%, marking a 19-month high and surpassing market expectations of 3.1%.
This acceleration in core inflation is particularly significant as it’s closely monitored by the Bank of Japan (BOJ) for monetary policy decisions.
Energy costs remained a significant contributor to inflation, with electricity prices up 18% and gas costs rising 6.8% year-on-year.
The absence of energy subsidies since May 2024 has kept these prices elevated, impacting household budgets.
Other sectors also experienced price increases, including housing (0.8%), clothing (2.8%), transport (2.0%), furniture and household items (3.4%), healthcare (1.8%), and miscellaneous items (1.4%).
However, communication prices continued to decline (-0.3%), as did education costs (-1.1%).
On a monthly basis, the Consumer Price Index (CPI) rose by 0.5%, following December’s 14-month high of 0.6%.
This persistent inflationary pressure may influence the BOJ’s monetary policy stance.
With core inflation consistently above the central bank’s 2% target for an extended period, speculation is growing about potential further interest rate hikes.
The BOJ’s recent shift away from ultra-loose monetary policy, including a rate hike to 0.5% in January, suggests a continued normalisation of monetary settings may be on the horizon.
However, the BOJ must balance inflation concerns with supporting economic growth, especially given the recent GDP data showing a deceleration in full-year growth projections for 2024.
As global economic uncertainties persist, including potential impacts from US trade policies, the BOJ’s path forward remains complex and closely watched by market participants.
Source: Trading Economics