Day Trading in Turkey



Rapid economic growth, improving electronic infrastructure, and rising interest in financial markets mean that short-term trading in Turkey is taking off.
This guide discusses how day trading in Turkey works, explaining the regulatory framework, tax regime, and revealing information on the country’s stock market. It also provides a hypothetical example of a share trade.
Quick Introduction
- Short-term trading is becoming rapidly popular in Turkey, where investors pay income tax of between 15% and 40%.
- Equities are exchanged on the Borsa Istanbul (BIST), with trading generally taking place between 10:00 and 18:00 Turkey Time (TRT).
- Financial markets are overseen by the Capital Markets Board of Turkey (CMB), a ‘yellow-tier’ regulator according to DayTrading.com’s Regulation & Trust Rating.
Top 4 Brokers In Turkey
These 4 trading platforms are a cut above the rest for active traders in Turkey following testing:
Day Trading Platforms in Turkey
What Is Day Trading?
Day traders in Turkey have a broad selection of financial securities to choose from, with the aim to profit from short-term market fluctuations.
You can deal in stocks, forex, bonds, or cryptocurrencies, to name just a handful, with CFD trading in Turkey also proving a particularly popular derivative.
The Borsa Istanbul (BIST) is the venue for share trading in Turkey. Investors can also deal in other financial securities here like bonds, derivatives (including futures and options), exchange-traded funds (ETFs), precious metals and diamonds.
The stock exchange’s leading index is the Borsa Istanbul 30 Index, or BIST 30 for short. In operation since 1996, it includes major multinational companies such as banking group Garanti BBVA, conglomerate Koç Holding, and travel giant Turkish Airlines.
Is Day Trading Legal In Turkey?
Yes. All financial market dealings are regulated by the Capital Markets Board of Turkey (CMB), whose mission statement is “to make innovative regulations, and perform supervision with the aim of ensuring fairness, efficiency and transparency in Turkish capital markets, and improving their international competitiveness.”
To preserve Turkey’s financial system and safeguard traders, the CMB oversees the market in accordance with the country’s Capital Markets Law. Its role is to introduce regulations, supervise markets and financial companies, and introduce enforcement action if appropriate.
Online brokers should also be approved by the CMB to do business in Turkey.
Unfortunately, this regulator does not provide a list of licensed companies, so you may want to consider firms that are also approved in other well-regulated territories (like the European Union, UK or US) so as to better avoid scammers.
How Is Day Trading Taxed In Turkey?
Day traders must pay personal income tax on any profits they make. Earnings must be declared to Turkey’s Revenue Administration, the body responsible for administering the country’s tax system and collecting payments.
The amount of income tax an individual is liable for is progressive according to one’s earnings. The rate varies between 15% and 40%, more details of which can be found here.
Getting Started
There are three main steps you must undertake to begin dealing in Turkey’s financial markets:
- Find a top day trading broker in Turkey. The first thing to consider is whether the broker is regulated by the CMB, or at the very least by a regulator in a mature economic region or country. Having done this, consider other factors like the user-friendliness of the trading platform, the range of tradeable securities, and the level of available leverage (a popular component of many active trading strategies).
- Open an account. When you’ve found a broker you like, you’ll need to open a trading account with them. You will need to answer a series of questions and provide proof of identification and address, such as a Turkish ID card. This process should take no longer than about 10 minutes, although it may take longer depending on the broker’s procedures and the completeness of the submitted documentation.
- Deposit funds. The final step is to put some liras in your account to trade with. Depositing with a debit card, through a wire transfer, or with an online payment provider (like PayPal) are the most common forms of payment, though the availability of deposit methods may differ from broker to broker.
A Trade In Action
With these steps completed, you’ll be ready to begin trading financial securities in Turkey. Here’s an example of what a short-term stock trade on the BIST 30 might look like.
The Background
My strategy is to profit from the Central Bank of the Republic of Turkey’s (CBRT) next interest rate announcement. I intend to do this by purchasing shares in one of the country’s biggest banks, of which there are several on the BIST 30 for me to choose from.
I decide to take a long position on Türkiye İş Bankası. Thanks to its high trading volumes, trading this stock can be especially cost-effective due to narrower bid and ask spreads than less-liquid companies. It’s also typically easier to enter and exit positions with popular shares like this.
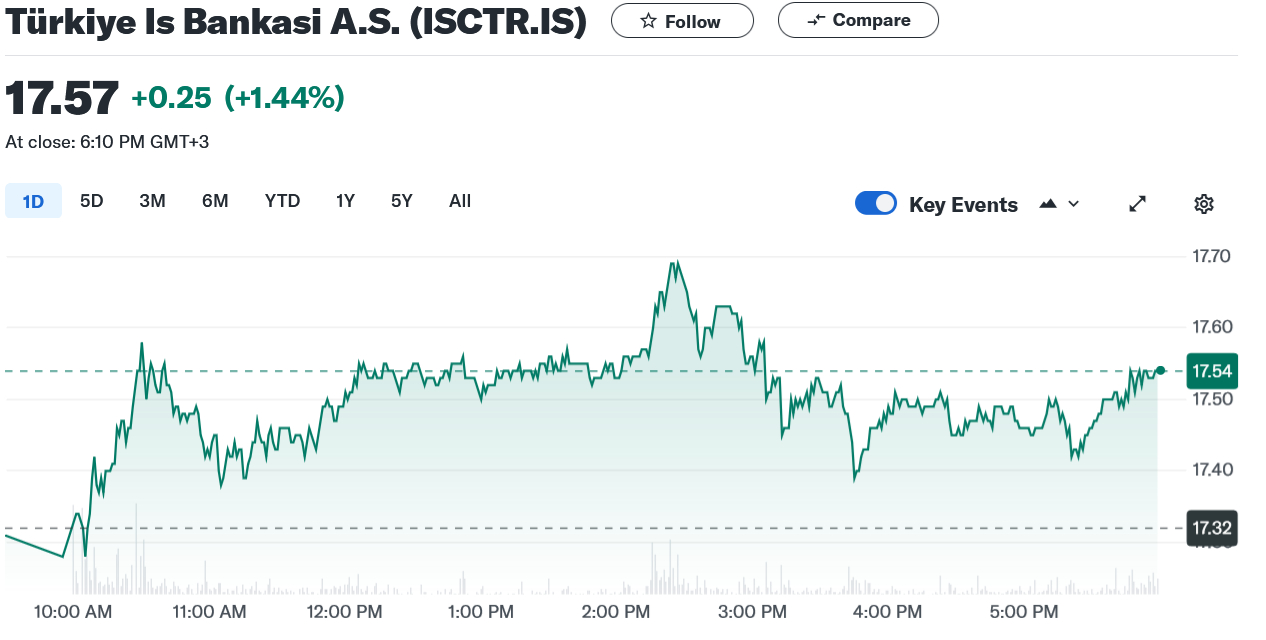
After carrying out some research, I conclude that the CBRT is likely to keep its benchmark rate on hold. This differs from the broader market, which is pricing in a potential rate cut of 0.25%.
If I’m correct, Türkiye İş Bankası’s share price could rise. This is because higher interest rates provide a boost to bank profits. They widen the margin between the money financial institutions make from borrowers and what they pay to savers (known as the net interest margin, or NIM).
My next step is to conduct technical analysis, using price and volume charts to help me get a better understanding of potential market movements following the CBRT’s announcement.
The Trade
With my preparation over, I’m ready to place the trade using my broker’s online trading platform. My plan is twofold: to place a ‘take profit’ order and a ‘stop loss’ instruction.
The ‘take profit’ order will automatically close my position if Türkiye İş Bankası’s shares rise to a specified level, thus locking in any profits. The ‘stop loss,’ on the other hand, will exit my trade if the bank unexpectedly drops to a particular price.
Combined, these tools allow me to effectively manage risk.
At 13:55 TRT – five minutes before the CBRT’s announcement – I sit down and punch in my orders. With Türkiye İş Bankası trading at 17.45 lira per share, I place my ‘take profit’ at 17.59 lira and my ‘stop loss’ at 17.38 lira.
Shortly afterwards, the central bank announces that interest rates have been held, as I expected. Within half an hour, Türkiye İş Bankası reaches 17.59, closing my position, and giving me a profit of 0.14 lira (or 14 kuruş).
Bottom Line
Day trading in Turkey is gaining popularity due to the country’s growing economy and developing digital framework. Investors can trade a variety of securities – some of which change hands on the BIST exchange – and financial activities are overseen by the country’s regulator.
Short-term trading can be highly risky, and the existence of fraudulent actors in Turkey (like any region) means it is critical that traders conduct thorough research and due diligence.
To get started, turn to DayTrading.com’s choice of the top day trading providers in Turkey.
Recommended Reading
Article Sources
- Borsa Istanbul (BIST)
- Trading Hours - BIST
- Capital Markets Board of Turkey (CMB)
- Borsa Istanbul 30 Index - BIST
- Tax Guide – Presidency of the Republic of Turkey Investment Office
- Turkey Time – Time And Date
- Revenue Administration
- Central Bank of the Republic of Turkey’s (CBRT)
The writing and editorial team at DayTrading.com use credible sources to support their work. These include government agencies, white papers, research institutes, and engagement with industry professionals. Content is written free from bias and is fact-checked where appropriate. Learn more about why you can trust DayTrading.com



