Position Trading


Position trading could be considered over other strategies if you have a longer trading horizon, a preference for reduced trading frequency, and a willingness to perform in-depth fundamental analysis. It’s also advantageous if you are seeking to capitalize on significant, sustained price trends in the market.
This guide to position trading unpacks the pros and cons of this system and explains how it compares to other investment approaches, to help you select the strategy that aligns best with your objectives.
Quick Introduction
- Position trading is applicable to various markets, encompassing stocks, commodities, indices, and forex.
- Position trading involves holding assets for months to years, aiming to profit from significant price movements.
- Although akin to investing, position trading differs by allowing short selling by not possessing the underlying asset.
- Position trading demands fewer trades compared to day trading or swing trading, reducing transaction costs and emotional stress.
- Effective risk management, including stop-loss orders and diversification, is crucial to mitigate potential losses during extended holding periods.
Best Position Trading Brokers
We recommend these 4 brokers for position trading:
Understanding Position Trading
Position trading is a strategy that offers several advantages and may be particularly appealing if you do not want to constantly monitor the markets or engage in the frequent trading that day or swing trading demands.
Position trading closely resembles traditional investing, with a significant distinction: buy-and-hold investing is restricted to long positions, whereas position trading provides the flexibility to employ a diverse array of trading instruments, including derivatives such as CFDs that allow both long and short speculation.
Position trading distinguishes itself from day and swing trading primarily through the extended timeframes involved. While day trading requires you to execute trades within a single day and swing trading requires holding positions for a few days to several weeks, position trading adopts a longer-term perspective and places fewer trades.
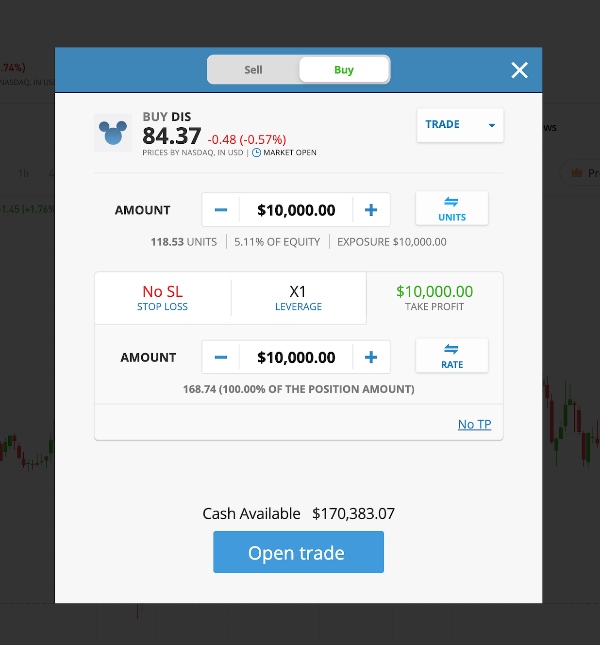
The primary reason to consider position trading is the longer trading horizon it entails. Positions are held for extended periods, often ranging from several months to years. This long-term perspective allows you to ride out short-term market fluctuations and focus on capturing larger price trends that can develop over time.
Another key benefit of position trading is the emphasis on fundamental analysis. You typically base your trading decisions on research into macroeconomic factors, company financials, and other relevant data. This fundamental approach can help you to make informed, well-reasoned investment choices, as opposed to relying solely on technical analysis or market sentiment.
Position trading also offers the advantage of reduced trading frequency. Since you hold positions for extended periods, you incur fewer transaction costs and may experience lower emotional stress associated with frequent trading.
While it may require patience to see the results of your trading fully, the potential for substantial returns over the long run can be a compelling enough reason to consider position trading.
However, it’s essential to note that this strategy also carries its own set of risks, including the potential for extended drawdowns, so it’s crucial to have a well-defined risk management plan in place.
Position Trading Strategies
Position trading typically involves a focus on long-term trading. While there isn’t a one-size-fits-all strategy for position trading, here are some popular approaches:
- Trend Following: Look for assets that are in long-term trends and aim to capitalize on the continuation of these trends. This strategy involves buying assets that are in uptrends or short-selling those in downtrends.
- Value Trading: Value-oriented trading seeks assets that you believe are undervalued based on fundamental analysis. You trade these assets with the expectation that their true value will be recognized over time.
- Momentum Trading: Momentum trading focuses on assets that are exhibiting strong price momentum, often driven by news, earnings reports, or other factors. The aim is to ride the momentum for an extended period.
- Cyclical Trading: You may target assets or sectors that are cyclical in nature, buying when they are out of favor and waiting for the upswing in their respective cycles.
- Sector Rotation: This strategy involves rotating into sectors or industries that are expected to perform well in the long term based on economic or market conditions.
- Options Hedging: Options can be traded to hedge your positions or generate additional income while maintaining long-term trades.
An Example Position Trade
Here is an example of how to make a position trade in the foreign exchange (forex) market. Note that this example is simplified for illustration purposes.
Scenario
Let’s say you’ve conducted extensive fundamental analysis on the EUR/USD currency pair. After your research, you believe that the euro (EUR) will appreciate against the U.S. dollar (USD) over the next several months due to positive economic developments in the Eurozone and relative stability in the U.S. economy.
Entry
In January, you decide to enter a long position in EUR/USD at an exchange rate of 1.1500. You commit $10,000 to this trade. Your expectation is that the EUR will strengthen against the USD over the long term.
Stop-loss and take-profit orders
To manage risk, you set a stop-loss order at 1.1300, which means you are willing to tolerate a 200-pip (0.0200) loss per unit. Additionally, you set a take-profit order at 1.1800, aiming to capture a 300-pip gain per unit.
These levels are determined based on your risk tolerance and the potential price movements you anticipate.
Holding period
As a position trade, you plan to hold this trade for several months, or possibly even longer, to give the market time to reflect your fundamental analysis.
Monitoring and adjustments
Over the following months, you periodically review the trade to ensure it remains aligned with your analysis. You pay attention to economic reports, central bank announcements, and any significant geopolitical events that may impact the EUR/USD exchange rate.
Exit
In June, the exchange rate for EUR/USD reaches your take-profit level of 1.1800. At this point, you decide to close the position, realizing a 300-pip profit per unit. Your $10,000 investment has grown to $13,000, resulting in a $3,000 profit before transaction costs (commissions and overnight fees).
Risk Management Plan
Position trading involves extended holding periods, so it’s critical to have a well-defined risk management plan to navigate the potential challenges and market fluctuations that may occur over months or even years.
Here is a risk management plan to help your position trading:
- Portfolio Diversification: Spread your trades across various asset classes and sectors to reduce exposure to any single investment. Diversification can help mitigate the impact of underperforming assets.
- Position Sizing: Determine the appropriate size for each position based on your risk tolerance and the percentage of your portfolio you’re willing to allocate. Avoid over-concentration in a single position.
- Stop-Loss Orders: Implement stop-loss orders for each position to establish predefined exit points in case the trade moves against you. Set these levels based on technical or fundamental factors, ensuring they align with your overall risk tolerance.
- Risk Assessment: Evaluate the potential risk and reward of each trade. Ensure that the potential reward justifies the risk you are taking. Aim for a minimum of a 2:1 risk-reward ratio.
- Position Monitoring: Regularly review your positions and stay updated on market developments and news that may impact your trades. Be prepared to adjust or exit positions based on new information.
- Hedging Strategies: Consider using hedging instruments, such as options or inverse ETFs, to protect your portfolio during market downturns or unforeseen events.
- Contingency Planning: Develop a clear set of contingency plans for various adverse scenarios, such as market crashes, unexpected geopolitical events, or economic downturns. Outline specific actions you will take in response to these events, including adjusting stop-loss levels, hedging strategies, or even exiting certain positions. Being prepared for unexpected developments is essential for safeguarding your portfolio in the face of unforeseen challenges.
- Emotional Discipline: Maintain emotional discipline and stick to your trading plan. Avoid impulsive decisions driven by fear or greed. Stay focused on your long-term objectives and avoid excessive trading.
- Record Keeping: Maintain detailed records of all your trades, including entry and exit points, rationale for the trade, and any relevant news or events. This documentation can help you learn from your experiences, identify patterns in your decision-making, and improve your trading strategy over time. It also serves as a valuable resource for tax purposes and future planning.
- Risk Capital Allocation: Only use funds that you can afford to lose without affecting your overall financial well-being. Never use money that you cannot afford to lose.
Pros And Cons Of Position Trading
Pros
- Long-Term Profit Potential: The biggest advantage of position trading is that it allows you to capture significant price trends over extended periods, offering the potential for substantial profits when these trends materialize.
- Reduced Stress: Short-term market volatility and news events don’t necessarily affect position trades, leading to reduced emotional stress compared to shorter-term trading strategies like day trading.
- Lower Transaction Costs: Position trading typically involves fewer trades, resulting in lower transaction costs, including commissions and spreads, which can eat into profits.
- Fundamental Analysis: This strategy emphasizes fundamental analysis, which can provide a deeper understanding of the assets being traded and potentially lead to more informed trading decisions.
- Time Efficiency: You do not need to monitor the markets as closely as day or swing trading, making it suitable if you have a busy schedule or other commitments.
Cons
- Long Holding Periods: Extended holding periods can tie up capital for months or years, limiting your ability to use it for other investment opportunities.
- Market Risk: Position trading exposes you to market risk over the entire holding period, which means you must be prepared to weather market downturns and potential losses.
- Missed Short-Term Opportunities: You may miss out on short-term profit opportunities that can arise from rapid price movements and market events.
- Potential For Larger Losses: Extended holding periods can result in more substantial losses if the market moves against your positions, and stop-loss orders might not always protect you from significant declines.
- Patience Required: Position trading requires a great deal of patience, as it can take time to see returns on investments. Impatience can lead to frustration or to making impulsive decisions.
Bottom Line
Position trading, while approachable, demands a solid grasp of market dynamics and proficient fundamental analysis skills for mastery. Position trading thrives in a trending market, but when the market is stagnant, moving sideways, or displaying erratic fluctuations, day or swing trading may offer a competitive edge.
If you opt to use a position trading strategy, it’s crucial to consider both its advantages and drawbacks, as outlined in our guide. Always adhere to prudent risk management principles in your short and long trades, and remember to hone your skills through practice in a demo account before committing real capital.
FAQ
What Is Position Trading?
The definition of position trading is when traders hold an investment for a long period of time with the expectation that the asset will rise in value. Position traders focus on long-term price moves by analyzing trends and fundamental events.
Is Position Trading Suitable For Beginners?
It can be, as long as you have a long-term outlook and patience. It’s less demanding in terms of time and trading frequency, but still requires a solid understanding of the markets and risk management.
Is Position Trading Profitable?
Only if you have a well-defined strategy, conduct thorough research, and exercise discipline. Profits typically accrue over the long term as you try to capture significant price trends, but success hinges on careful risk management, a patient approach, and the ability to weather market fluctuations. Similar to all strategies, it carries inherent risks and doesn’t guarantee profits.
Is Position Trading Legal?
Position trading is a legal form of trading in most jurisdictions. However, always ensure you are trading with a reputable broker, in order to keep your funds secure. You may also need to check in your local jurisdiction for any restrictions on trading approaches.
What Is The Difference Between Position Trading And Day Trading?
Position trading involves holding assets for months or years, focusing on long-term trends and fundamental analysis. Day trading, on the other hand, involves opening and closing positions within the same trading day, aiming for short-term price movements and relying heavily on technical analysis.
Position trading offers lower stress, reduced trading frequency, and less need for constant monitoring, while day trading requires quick decision-making and frequent trading activity, with higher stress levels and risk.
What Is The Difference Between Position Trading And Swing Trading?
Position trading and swing trading both aim to profit from longer-term price trends, but they differ in their holding periods. Position trading involves holding assets for months to years, while swing trading holds positions for days to a few weeks.
Position trading focuses on macroeconomic factors and fundamentals, whereas swing trading often relies more on technical analysis and shorter-term trends.
What Is The Difference Between Position Trading And Investing?
Position trading and investing both involve a longer-term approach, but they differ in their objectives. Position trading seeks to profit from price trends over months to years and often involves more active management.
Investing typically has a buy-and-hold strategy with a focus on long-term wealth accumulation and income generation through dividends or interest, often requiring less active monitoring and trading.
Article Sources
- Fundamental Analysis and Position Trading, Thomas N. Bulkowski, 2012
- Position Trading Simplified, Tranquil Trader, 2021
The writing and editorial team at DayTrading.com use credible sources to support their work. These include government agencies, white papers, research institutes, and engagement with industry professionals. Content is written free from bias and is fact-checked where appropriate. Learn more about why you can trust DayTrading.com



