Best Market Maker Brokers


Market maker brokers are companies that buy and sell financial assets with the use of their own inventories. They allow markets to operate smoothly by supplying deep liquidity and provide important benefits for short-term traders.
This guide will explain how they work, plus the advantages and disadvantages you can experience by day trading with a market maker broker. We’ve also evaluated a long row of companies to bring you our pick of the best market maker brokers.
Best Market Maker Brokers 2025
These are the top market-making brokers based on our exhaustive reviews:
Here is a short overview of each broker's pros and cons
- Plus500 US - Plus500 is a well-established broker that entered the US market in 2021. Authorized by the CFTC and NFA, it provides futures trading on forex, indices, commodities, cryptocurrencies, and interest rates. With a 10-minute sign-up, a manageable $100 minimum deposit, and a straightforward web platform, Plus500 continues to strengthen its offering for traders in the US.
- OANDA US - OANDA is a popular brand offering exceptional execution, low deposit requirements and advanced charting and trading platform features. The top-rated brand has over 25 years of experience and is regulated by trusted agencies, including the NFA/CFTC. Around the clock support is available for short-term traders, alongside flexible contract sizes and automated trade executions.
- Firstrade - Firstrade is a US-headquartered discount broker-dealer with authorization from the SEC. The company is also a member of FINRA/SIPC. With welcome bonuses, powerful tools and apps, plus commission-free trading, Firstrade Securities is a popular and top-tier online brokerage. It is also quick and easy to open a new account.
- AvaTrade - Established in 2006, AvaTrade is a leading forex and CFD broker trusted by over 400,000 traders. Operating under regulation in 9 jurisdictions, AvaTrade processes an impressive 2+ million trades each month. Through like MT4, MT5, and its proprietary WebTrader, the broker provides a growing selection of 1,250+ instruments. Whether it’s CFDs, AvaOptions, or the more recent AvaFutures, short-term traders at all levels will find opportunities. With terrific education and 24/5 multilingual customer support, AvaTrade delivers the complete trading experience.
- XM - XM is a globally recognized forex and CFD broker with 10+ million clients in 190+ countries. Since 2009, this trusted broker has been delivering low trading fees across its growing roster of 1000+ instruments. It’s also highly regulated, including by ASIC and CySEC and offers a comprehensive MetaTrader experience.
- Exness - Established in 2008, Exness has maintained its position as a highly respected broker, standing out with its industry-leading range of 40+ account currencies, growing selection of CFD instruments, and intuitive web platform complete with useful extras like currency convertors and trading calculators.
Best Market Maker Brokers Comparison
| Broker | Market Maker | Minimum Deposit | Investment Offering | Trading Platforms | Financial Regulators |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plus500 US | ✔ | $100 | Futures on Cryptocurrencies, Metals, Agriculture, Forex, Interest rates, Energy, Equity Index future contracts | WebTrader, App | CFTC, NFA |
| OANDA US | ✔ | $0 | Forex, Crypto with Paxos (Cryptocurrencies are offered through Paxos. Paxos is a separate legal entity from OANDA) | OANDA Trade, MT4, TradingView, AutoChartist | NFA, CFTC |
| Firstrade | ✔ | $0 | Stocks, ETFs, Options, Mutual Funds, Bonds, Cryptos, Fixed | TradingCentral | SEC, FINRA |
| AvaTrade | ✔ | $100 | CFDs, Forex, Stocks, Indices, Commodities, ETFs, Bonds, Crypto, Spread Betting, Futures | WebTrader, AvaTradeGO, AvaOptions, AvaFutures, MT4, MT5, AlgoTrader, TradingCentral, DupliTrade | ASIC, CySEC, FSCA, ISA, CBI, FSA, FSRA, BVI, ADGM, CIRO, AFM |
| XM | ✔ | $5 | CFDs, Forex, Stocks, Commodities, Indices, Thematic Indices, Precious Metals, Energies | MT4, MT5, TradingCentral | ASIC, CySEC, DFSA, IFSC |
| Exness | ✔ | $10 | CFDs, Forex, Stocks, Indices, Commodities, Crypto | Exness Trade App, Exness Terminal, MT4, MT5, TradingCentral | CySEC, FCA, FSCA, CMA, FSA, CBCS, BVIFSC, FSC, JSC |
Plus500 US
"Plus500 US stands out as an excellent choice for beginners, offering a very user-friendly platform, low day trading margins, and access to the Futures Academy to enhance trading skills. Its powerful tools and reliable service helped it scoop second place in DayTrading.com's annual 'Best US Broker' award."
Michael MacKenzie, Reviewer
Plus500 US Quick Facts
| Bonus Offer | Welcome Deposit Bonus up to $200 |
|---|---|
| Demo Account | Yes |
| Instruments | Futures on Cryptocurrencies, Metals, Agriculture, Forex, Interest rates, Energy, Equity Index future contracts |
| Regulator | CFTC, NFA |
| Platforms | WebTrader, App |
| Minimum Deposit | $100 |
| Minimum Trade | 0.0 Lots |
| Account Currencies | USD |
Pros
- The Futures Academy is an excellent resource for new traders with engaging videos and easy-to-follow articles, while the unlimited demo account is great for testing strategies
- Plus500 is a publicly traded company with a good reputation, over 24 million traders, and a sponsor of the Chicago Bulls, instilling a sense of trust
- The straightforward account structure, pricing model and web platform offer an easier route into futures trading than rivals like NinjaTrader
Cons
- Despite competitive pricing, Plus500 US lacks a discount program for high-volume day traders, a scheme found at brokers like Interactive Brokers
- Although support response times were fast during tests, there is no telephone assistance
- Plus500 US does not offer social trading capabilities, a feature available at alternatives like eToro US which could strengthen its offering for aspiring traders
OANDA US
"OANDA remains an excellent broker for US day traders seeking a user-friendly platform with premium analysis tools and a straightforward joining process. OANDA is also heavily regulated with a very high trust score."
Jemma Grist, Reviewer
OANDA US Quick Facts
| Demo Account | Yes |
|---|---|
| Instruments | Forex, Crypto with Paxos (Cryptocurrencies are offered through Paxos. Paxos is a separate legal entity from OANDA) |
| Regulator | NFA, CFTC |
| Platforms | OANDA Trade, MT4, TradingView, AutoChartist |
| Minimum Deposit | $0 |
| Minimum Trade | 0.01 Lots |
| Leverage | 1:50 |
| Account Currencies | USD, EUR, GBP, CAD, AUD, JPY, CHF, HKD, SGD |
Pros
- OANDA is a reliable, trustworthy and secure brand with authorization from tier-one regulators including the CFTC
- The broker offers a transparent pricing structure with no hidden charges
- The broker's API facilitates access to 25 years of deep historical data and rates from 200+ currencies
Cons
- There's only a small range of payment methods available, with no e-wallets supported
- It's a shame that customer support is not available on weekends
- The range of day trading markets is limited to forex and cryptos only
Firstrade
"Firstrade is perfect for beginners looking to trade US stocks with zero commissions. There is a wealth of free education plus premium-quality research, notably through its latest FirstradeGPT tool, plus trading ideas from Morningstar, Briefing.com, Zacks and Benzinga."
William Berg, Reviewer
Firstrade Quick Facts
| Bonus Offer | Deposit Bonus Up To $4000 |
|---|---|
| Demo Account | No |
| Instruments | Stocks, ETFs, Options, Mutual Funds, Bonds, Cryptos, Fixed |
| Regulator | SEC, FINRA |
| Platforms | TradingCentral |
| Minimum Deposit | $0 |
| Minimum Trade | $1 |
| Account Currencies | USD |
Pros
- One of the first brokers to add AI-powered analysis through FirstradeGPT
- Enhanced stock trading environment with overnight trading and fractional shares added
- Excellent broker for budget-conscious traders with low OTC fees
Cons
- Customer support still needs work following testing with no 24/7 assistance
- No demo/paper trading account found at over 90% of alternatives evaluated
- Visa credit/debit card deposits and withdrawals are not accepted
AvaTrade
"AvaTrade offers active traders everything they need: an intuitive WebTrader, powerful AvaProtect risk management, a smooth 5-minute sign-up process, and dependable support you can rely on in fast-moving markets."
Jemma Grist, Reviewer
AvaTrade Quick Facts
| Bonus Offer | 20% Welcome Bonus up to $10,000 |
|---|---|
| Demo Account | Yes |
| Instruments | CFDs, Forex, Stocks, Indices, Commodities, ETFs, Bonds, Crypto, Spread Betting, Futures |
| Regulator | ASIC, CySEC, FSCA, ISA, CBI, FSA, FSRA, BVI, ADGM, CIRO, AFM |
| Platforms | WebTrader, AvaTradeGO, AvaOptions, AvaFutures, MT4, MT5, AlgoTrader, TradingCentral, DupliTrade |
| Minimum Deposit | $100 |
| Minimum Trade | 0.01 Lots |
| Leverage | 1:30 (Retail) 1:400 (Pro) |
| Account Currencies | USD, EUR, GBP, CAD, AUD |
Pros
- Support at AvaTrade performed excellently during testing, with response times of 3 minutes and localized support in major trading jurisdictions, including the UK, Europe and the Middle East.
- The WebTrader excelled in our hands-on tests, sporting a user-friendly interface for beginners, complete with robust charting tools like 6 chart layouts and 60+ technical indicators.
- AvaTrade continues to enhance its suite of products, recently through AvaFutures, providing an alternative vehicle to speculate on over 35 markets with low day trading margins.
Cons
- AvaTrade’s WebTrader has improved, but work is still needed in terms of customizability – frustratingly widgets like market watch and watchlists can’t be hidden, moved, or resized.
- While signing up is a breeze, AvaTrade lacks an ECN account like Pepperstone or IC Markets, which provides the raw spreads and ultra-fast execution many day traders are looking for.
- Although the deposit process itself is smooth, AvaTrade still doesn’t facilitate crypto payments, a feature increasingly offered by brokers like TopFX, which caters to crypto-focused traders.
XM
"With a low $5 minimum deposit, advanced charting platforms in MT4 and MT5, expanding range of markets, and a Zero account offering spreads from 0.0, XM provides all the essentials for active traders, even earning our ‘Best MT4/MT5 Broker’ award in recent years."
Christian Harris, Reviewer
XM Quick Facts
| Bonus Offer | $30 No Deposit Bonus When You Register A Real Account |
|---|---|
| Demo Account | Yes |
| Instruments | CFDs, Forex, Stocks, Commodities, Indices, Thematic Indices, Precious Metals, Energies |
| Regulator | ASIC, CySEC, DFSA, IFSC |
| Platforms | MT4, MT5, TradingCentral |
| Minimum Deposit | $5 |
| Minimum Trade | 0.01 Lots |
| Leverage | 1:1000 |
| Account Currencies | USD, EUR, GBP, JPY |
Pros
- XM stands out for its commitment to trader education, with a wealth of well-presented resources, including webinars, tutorials, and even real-time trading sessions through XM Live.
- XM’s Zero account is ideal for day trading with spreads from 0.0 pips, 99.35% of orders executed in <1 second, and no requotes or rejections.
- XM’s customer support has delivered over years of testing, with 24/5 assistance in 25 languages, response times of <2 minutes and now a growing Telegram channel.
Cons
- XM relies solely on the MetaTrader platforms for desktop trading, so there’s no in-house downloadable or web-accessible solution for a more beginner-friendly user experience with unique features.
- While the XM app stands out for its usability and exclusive copy trading products, the selection of technical analysis tools needs to be improved to meet the needs of advanced traders.
- Although trusted and generally well-regulated, the XM global entity is registered with the weak IFSC regulator and UK clients are no longer accepted, reducing its market reach.
Exness
"After slashing its spreads, improving its execution speeds and support trading on over 100 currency pairs with more than 40 account currencies to choose from, Exness is a fantastic option for active forex traders looking to minimize trading costs."
Christian Harris, Reviewer
Exness Quick Facts
| Demo Account | Yes |
|---|---|
| Instruments | CFDs, Forex, Stocks, Indices, Commodities, Crypto |
| Regulator | CySEC, FCA, FSCA, CMA, FSA, CBCS, BVIFSC, FSC, JSC |
| Platforms | Exness Trade App, Exness Terminal, MT4, MT5, TradingCentral |
| Minimum Deposit | $10 |
| Minimum Trade | 0.01 Lots |
| Leverage | 1:Unlimited |
| Account Currencies | USD, EUR, GBP, CAD, AUD, NZD, INR, JPY, ZAR, MYR, IDR, DKK, CHF, HKD, SGD, AED, SAR, HUF, BRL, NGN, THB, VND, UAH, KWD, QAR, KRW, MXN, KES, CNY |
Pros
- Highly competitive spreads, reduced for USOIL and BTCUSD in 2024, are available from 0 pips with low commissions from $2 per side.
- Fast and dependable 24/7 multilingual customer support via telephone, email and live chat based on hands-on tests.
- Improved execution speeds, now averaging under 25ms, offer optimal conditions for short-term traders.
Cons
- MetaTrader 4 and 5 are supported, but TradingView and cTrader still aren’t despite rising demand from active traders and integration at alternatives like Pepperstone.
- Apart from a mediocre blog, educational resources are woeful, especially compared to category leaders like IG which provide a more complete trading journey for newer traders.
- Retail trading services are unavailable in certain jurisdictions, such as the US and the UK, limiting accessibility compared to top-tier brokers like Interactive Brokers.
How Did We Choose The Best Market Maker Brokers?
The first and most important thing we checked is that the company is trusted.
The best indicator of a trustworthy broker is authorization from a creditable body, such as the Securities and Exchange Commission in the US or the Financial Conduct Authority in the UK.
This will help safeguard your capital, ensure you are receiving a high level of customer care, and reduce the risk of falling victim to conflicts of interest.
Following that:
- We evaluated the market maker broker’s costs in the form of bid/ask spreads, commissions and additional fees.
- We looked for companies that are transparent about their operations and pricing structure.
- We looked for brokers with a wide selection of assets and securities, ensuring you’ll have a range of opportunities and the ability to build a diverse portfolio.
- We tested the broker’s trading platform to make sure it’s enjoyable to use and that you can enter and exit positions quickly and easily.
- We selected brokers with helpful features for short-term traders, including technical analysis tools, trading guides and mobile apps that facilitate trading ‘on the go’
- We prioritized market maker brokers with excellent customer support based on our hands-on tests that consider the speed and quality of assistance.
- We investigated the amount of borrowed funds, known as leverage, that you can use to trade, as this can play an important role in day trading strategies.
Understanding Market Makers
Market makers play an essential part in trading that takes place on regulated financial exchanges. They act as the middleman between buyers and sellers of financial securities, and continuously quote prices during market hours, thus ensuring that a trade can always be executed.
The deep liquidity that these institutions provide is critical for financial markets. It allows assets to be purchased and offloaded without causing substantial price turbulence.
Furthermore, their presence ensures that short-term traders, such as day traders, can open and close positions more easily.
Market makers also act as the middlemen in over-the-counter trading, where buyers and sellers do business outside of a financial exchange.
Importantly, market makers are not the same as brokerages. While brokers bring buyers and sellers together and pass orders onto third-party liquidity providers, market makers create the marketplace for investors by buying and selling assets directly to and from them.
However, financial institutions can act as both market makers and brokers. Trading with one of these dual-role entities carries advantages for short-term traders, though you should be aware of potential conflicts of interest that may arise.
Notably, market maker brokers may have an inherent conflict of interest as they often take positions opposite to their clients, potentially profiting from client losses. They also control prices and execution, which can lead to practices like price manipulation and less favorable execution for traders.
Strict regulation means that these companies must establish robust procedures and systems to avert any such conflicts.
These include setting up Chinese walls (barriers between different divisions), establishing strict order routing rules, and conducting regular internal audits.
How Do Market Makers Work?
These institutions anticipate executing high volumes of buy and sell orders each day. And so they hold large inventories of assets, such as stocks, commodities, currencies and bonds, that they stand ready to trade from.
This function means that markets can keep moving by guaranteeing that a buyer and a seller can always find someone to do business with.
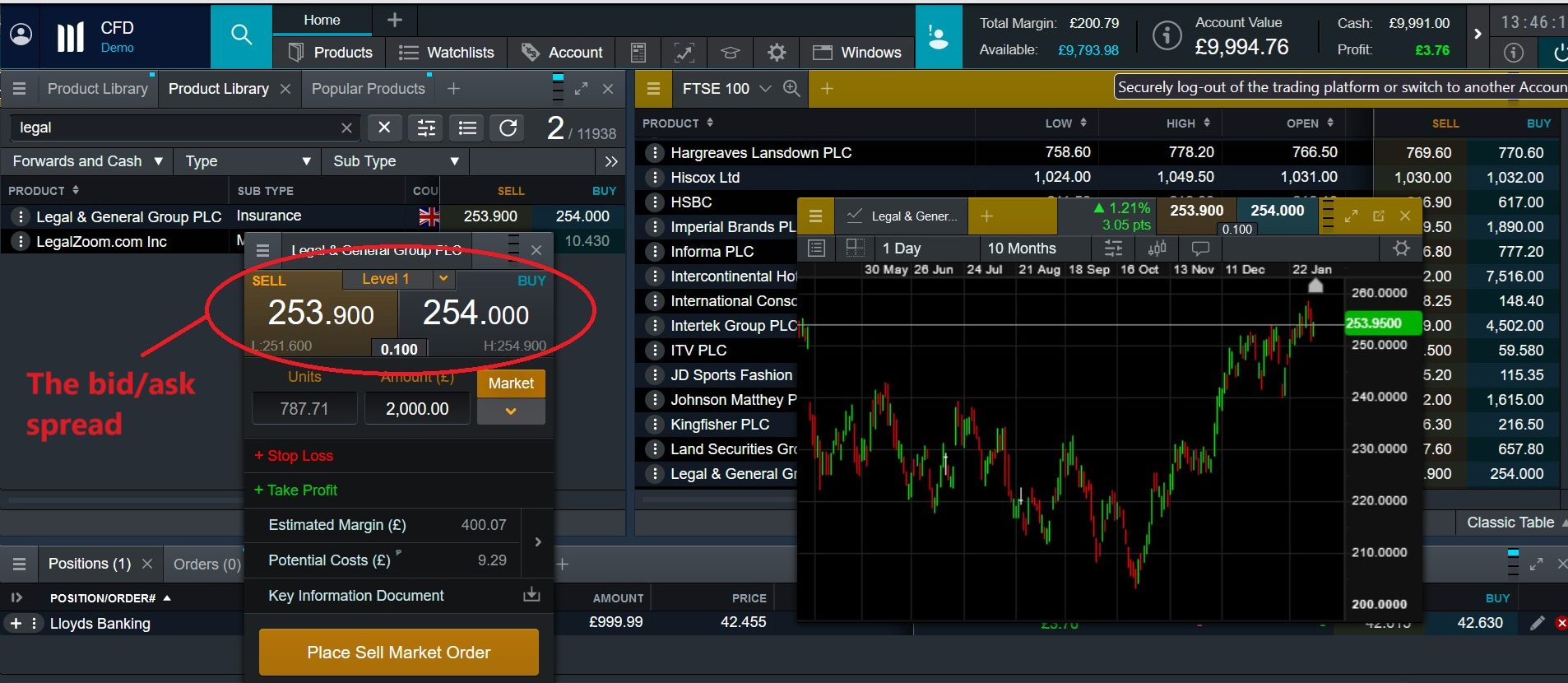
When markets are ‘illiquid,’ an investor may have difficulties locating another to make a trade. In these situations, the spread – in other words, the difference between the buy (or bid) and sell (or ask) prices – can be exceptionally high, resulting in greater costs to the trader.
How Do Market Maker Brokers Make Money?
Market-making brokers primarily generate profits through the bid/ask spread. They seek to buy at a lower bid price and sell at the higher ask price, and bank the difference in the process.
These institutions are still able to make money when liquidity is healthy and bid-ask spreads are kept to a minimum.
Whilst margins are small, the colossal volume of trades that are placed each day enables them to make a tidy profit.
Certain market makers will also charge fees or commissions to execute trades. However, a high level of competition means that these costs – along with the difference between bid and ask prices – do not become prohibitive for traders.
Even if a market maker charges a trading fee, this can often be lower than that imposed by other brokers (like agency brokers).
Example Trade
Let’s say that I wish to trade shares in Colin’s Computers using a market maker broker. I believe prices of the company will rise in price, and decide to buy 100 shares in the business to capitalize on this. The company currently trades at $50 per share.
To begin with, I’ll have a look at the bid and ask prices on my market-making broker’s trading platform. They are listed as:
- Bid price: $49.90
- Ask price: $50.10
This results in a bid/ask spread of $0.20.
When I place my buy order for 100 Colin’s Computers shares, the brokerage will match my instruction with existing sell orders on the market. If there is a seller who’s happy to offload their shares at $50.10, my order will be executed at this price.
In this case, how much profit would the market maker receive?
First off, let’s have a look at the total cost of the trade to me. This stands at $5,010 ($50.10 x 100 shares).
Now let’s assume that the market maker initially bought those shares for their inventory at the lower price of $49.90 each. Their profit would come in at $20 (the bid/ask spread of $0.20 x 100 shares).
Bottom Line
Deep liquidity is the key to straightforward and cost-effective trading. And by using market-making brokers, traders can enjoy an optimal dealing experience and improve their chances of making a profit.
However, using one of these brokerages to trade also presents risks that individuals need to be constantly mindful of. That’s why we recommend choosing one of our top-rated market maker brokers.
FAQ
What Is A Market Maker?
A market maker is a firm or broker that provides bids and offers of a two-sided market along with the market size of each. By trading on both sides of the market, these companies provide a platform for trading, making their money through spreads.
Do Market Maker Brokers Manipulate Prices?
Market maker brokers set their own bid/ask prices, which makes it possible for them to manipulate asset prices. However, competition is so stiff that spreads offered by market makers are generally tight.
Finding a market maker broker that is registered with a respected authority will help prevent you from being scammed or manipulated.
Do Market Maker Brokers Own Stock?
A market maker will buy stock from you and hold it until it finds another buyer. During this time, the broker does own that stock. However, they do not hold shares for their own benefit.
What Are The Advantages Of Trading With A Market Maker Broker?
Market maker brokers with healthy liquidity allow traders to enter and exit positions rapidly, thus enabling you to swiftly capitalize on trading opportunities that arise. This also helps reduce the threat of slippage, where the expected and actual prices of a trade differ due to timing issues.
Many of these brokers also offer fixed spreads, which appeal to beginners especially, providing a clear picture of how much a trade will cost.
What Are The Risks Of Trading With A Market Maker Broker?
While their operations are often closely observed by regulators, the potential for market-making brokers to act in their own interests at the expense of traders is always present.
Also, market makers may not provide the same level of price transparency as other brokers, such as electronic communication network (ECN) brokers.
Additionally, with ECN brokers, it is possible to trade prices at certain times with little or no spread. This means day traders can often get better prices with these companies than with market makers.





