Day Trading in India



India’s booming economy and improving digital infrastructure have driven interest in financial markets through the roof. In fact, the level of speculative activity like day trading has soared in recent years, prompting Indian regulators to introduce restrictions to protect investors.
Looking to start day trading in India? This guide for beginners will unpack trading in the Asian country, including an example of a short-term trade on an Indian stock. You’ll also learn about India’s regulatory and tax regimes.
Quick Introduction
- Day traders can deal in a wide variety of financial securities, including stocks, Indian currency pairs, and derivatives like options. India is home to the National Stock Exchange (NSE), one of the world’s fastest-growing stock trading venues.
- Financial markets are regulated by the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), which is a ‘yellow tier’ regulator under DayTrading.com’s Regulation & Trust Rating.
- Active traders may need to pay income tax on their speculative and/or non-speculative business income at a rate of up to 30% to India’s Income Tax Department.
Top 4 Brokers in India
After evaluating 224 platforms, these 4 brokers emerged as superior for day traders in India:
Day Trading Platforms in India
What Is Day Trading?
Day trading involves the frequent buying and selling of financial securities. Trades last anywhere from a few seconds to several hours and are typically closed on the same day to eliminate the risks associated with holding assets overnight.
Traders seek to profit from tiny changes in asset prices, and they tend to operate at times when market liquidity and volatility are high. By placing many trades throughout the day, investors can accumulate a large profit over the course of the trading session.
Due to its fast-paced nature, traders often use ‘take profit’ and ‘stop loss’ orders to automatically close their trades. These risk management tools allow them to secure profits or limit losses without having to constantly monitor the market.
What Assets Can I Trade?
Day traders in India can choose from a wide variety of assets.
The National Stock Exchange (NSE) is the preferred destination for day traders to deal equities thanks to its deep liquidity. This allows investors to open and close positions quickly and at low cost thanks to tight bid and ask spreads.
The exchange has some 2,900 company listings and is home to the benchmark NIFTY 50 index, one of the biggest in Asia. Major names here include conglomerate Reliance Industries, financial services giant HDFC Bank, and IT services provider Tata Consultancy.
The NSE also facilitates derivatives trading on shares, equity indices, forex, commodities and interest rates. Investors can exchange fixed-income products like government and corporate bonds as well.
Cryptocurrency trading became legal again in 2020 after the Supreme Court overturned a Reserve Bank of India (RBI) ban on digital currency exchanges.
Crypto trading remains unregulated, although the country’s position on the dealing of virtual assets is evolving. In 2021, the ‘Cryptocurrency and Regulation of Official Digital Currency Bill’ was drawn up. The law would seek to create an RBI-issued digital currency whilst prohibiting private cryptocurrencies.
Trading CFDs in India, meanwhile, is a legal grey area. Brokerages offering these high-risk products are not regulated in India, meaning traders need to look for overseas companies potentially foregoing legal protections.
Is Day Trading Legal In India?
Yes. Financial markets are primarily regulated by the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), which was established in 1988.
In its own words, its role is “to protect the interests of investors in securities and to promote the development of, and to regulate the securities market.”
To operate in India’s capital markets, service providers must apply for a licence with SEBI and adhere to its rules. Those that fall foul of regulations can be subject to enforcement action including fines and trading bans.
SEBI remains concerned about over-the-top speculation in India’s capital markets, and in August 2021 introduced ‘Peak Margin Rules’ to reduce excessive risk-taking and price volatility by restricting the use of leverage (borrowed funds).
Prior to the rules, margin requirements were based on end-of-the-day positions, allowing traders to build significant intraday positions without maintaining adequate margins.
Now, traders must maintain 100% of the required margin up front, with margin requirements based on the highest level of exposure during the trading session.
In July 2024, SEBI proposed restricting India’s booming options market as the latest chapter of its crackdown on excessive speculation.Plans include hiking trading margin requirements, raising minimum trading amounts, and reducing the number of contracts expiring each week.
How Is Day Trading Taxed In India?
The Indian Revenue Service (Income Tax) – which acts under the Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT) – is responsible for collecting taxes from active traders.
India’s tax year runs from 1 April to 31 March, and individuals must submit tax returns by 31 July the following year.
The IRS will classify the profits that active traders make as either speculative business income or, in the case of futures and options dealing, non-speculative business income.
Traders can offset non-speculative profits against business expenses like software charges and internet bills.
Income tax is charged at the following progressive rates on speculative and non-speculative business income:
| Income slabs | Income tax rate |
|---|---|
| Up to ₹300,000 | 0% |
| ₹300,000 to ₹600,000 | 5% on income exceeding ₹300,000 |
| ₹600,000 to ₹900,000 | ₹15,000 + 10% on income exceeding ₹600,000 |
| ₹900,000 to ₹1,200,000 | ₹45,000 + 15% on income exceeding ₹900,000 |
| ₹1,200,000 to ₹1,500,000 | ₹90,000 + 20% on income exceeding ₹1,200,000 |
| Above ₹1,500,000 | ₹150,000 + 30% on income exceeding ₹1,500,000 |
Traders who hold certain securities for more than one day (but less than 365 days) may also be liable to pay short-term capital gains tax of 15%.
Cryptocurrency traders pay a flat rate of 30% tax on capital gains, as well as a 1% tax deduction at source (TDS) on the sale of crypto assets exceeding ₹10,000 (in most cases).
With trading taxes in India remaining complex and evolving, I recommend consulting a professional tax advisor who can help ensure you meet your obligations and optimize your trading activities for tax purposes.
Getting Started
There are three steps you must take before you can start short-term trading in India:
- Pick a top day trading broker in India. Ensure that the brokerage you’re considering is licensed and listed on the SEBI website. Alternatively, choose one that is approved by a top-tier regulator in an overseas territory (like the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) in the UK). After this, consider factors such as the functionality of the broker’s trading platform, or Indian day trading app, the quality of its charting tools (TradingView is terrific for technical analysis), trading fees, and the amount of leverage on offer.
- Open an account. You’ll need to provide the brokerage with some personal details. You’ll also need to provide proof of identity and residence (such as a copy of your Aadhaar card) to open your account, while you can expect to be quizzed on your investing experience and trading goals. Brokers with INR accounts can make trading easier and more cost-effective for Indian residents.
- Deposit some Indian rupees. You’ll need some cash on account to start buying securities, which you should be able to do quickly and easily with a debit card or a bank transfer. Some brokerages may also allow you to deposit using an online payment provider such as Google Wallet or India’s Paytm.
A Day Trade In Action
With these boxes checked off, you’ll now be ready to start dealing in India’s financial markets. But what could a short-term trade look like?
Here’s an example of how a trade involving one of the NIFTY 50’s biggest companies might unfold.
The Background
My plan is to buy Bharti Airtel shares before the RBI makes its upcoming interest rate announcement, and to sell them shortly thereafter.
My expectation is that the central bank will cut its benchmark rate by 0.4%, to 5.6%. This differs from the 0.25% cut that the broader market is predicting.
If I’m correct, shares across the domestic telecommunications sector might rise in value. Multinational Bharti itself makes approximately 75% of its revenues from India, making it highly sensitive to RBI rate cuts that could stimulate consumer demand. Lower rates might also significantly reduce the loan costs of debt-heavy firms like telecoms operators.
Before placing my trade, I also carry out technical analysis on Bharti Airtel’s share price. Being able to successfully identify price trends and patterns is an essential part of short-term trading strategies.
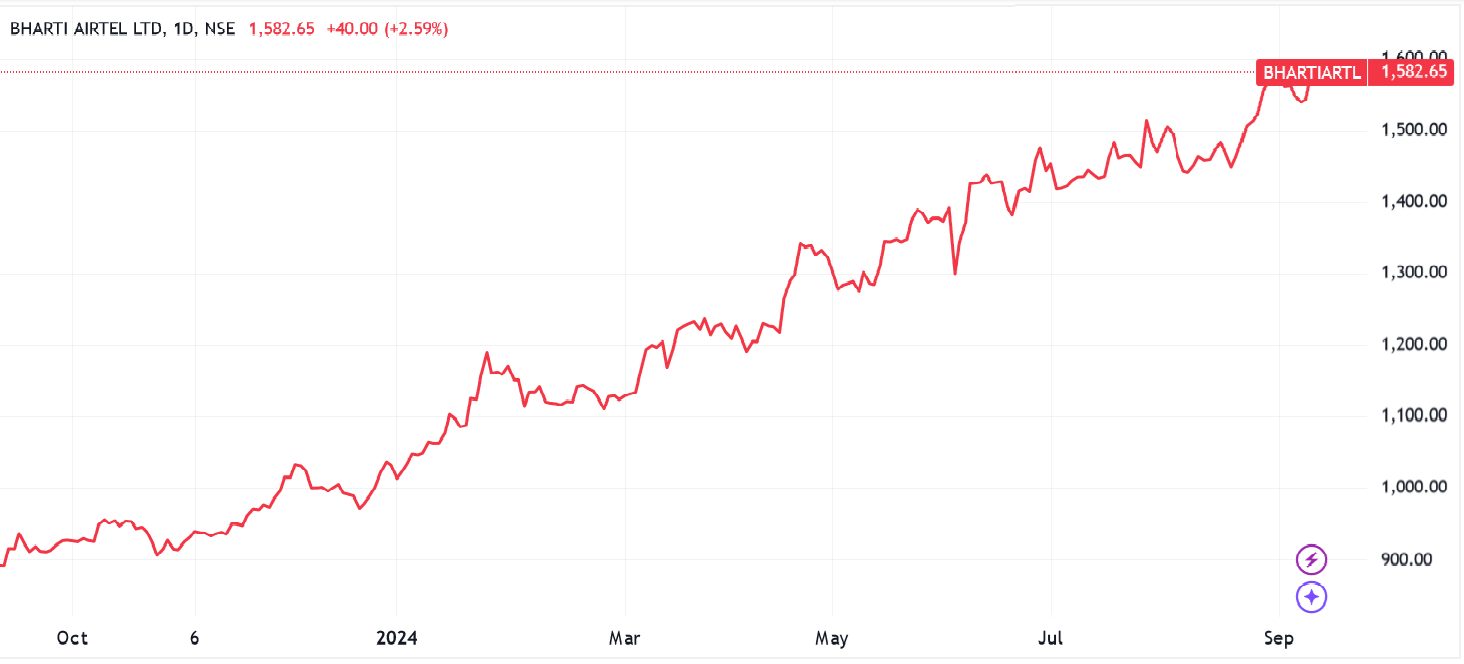
The Trade
With my plan drawn up, I open my trading platform at 09:50 IST, giving me 10 minutes to key in my trade before the central bank announcement.
At this time, I find Bharti Airtel shares changing hands at ₹1,582.65 each. So I set my ‘take profit’ instruction at ₹1,584.24 and my ‘stop loss’ order at ₹1,581.82. I then sit back and wait for the RBI’s news.
Within a few minutes, the news comes through that interest rates were cut by a forecast-beating 0.5%. This was also more than I’d predicted, and causes share prices across the NIFTY 50 to rally.
After about half an hour the Bharti share prices moves through ₹1,584.24, triggering my ‘take profit’ order and automatically closing my position. This leaves me with a profit of ₹1.59 for each share I bought.
Bottom Line
Rapid economic growth, combined with a surge in the number of online brokerages, has led to a boom in the number of day traders in India.
Investors can deal in a wide range of financial securities, although specific local rules exist for certain asset classes (like the banning of non-rupee trades in forex markets).
Regulators are stepping up restrictions to curb speculation, but on balance, India remains an attractive place to trade financial markets.
Always check that the broker you choose is licensed by SEBI or with a reputable overseas regulator, however, and only risk what you can afford to lose.
To get started, check out DayTrading.com’s selection of the best day trading platforms in India.
Recommended Reading
Article Sources
- National Stock Exchange (NSE)
- Our Products - NSE
- India Bans Cryptocurrency Trades – BBC News
- All You Need To Know About India’s Crypto Bill - Forbes
- India to Ban Private Cryptocurrencies and Launch Official Digital Currency – The Guardian
- Guide To Crypto Tax In India - CoinDCX
- Market Timings & Holidays - NSE
- Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI)
- SEBI's New Peak Margin Rules From Sept 1: How it Affects Traders – Economic Times
- SEBI’s Peak Margin Rules – Bajaj Broking
- India Markets Regulator Proposes Slew of Measures to Curb Options Trading Frenzy - Reuters
- Indian Revenue Service (Income Tax)
- NRI Taxation: Know the Income Tax Rates - ICICI Bank
The writing and editorial team at DayTrading.com use credible sources to support their work. These include government agencies, white papers, research institutes, and engagement with industry professionals. Content is written free from bias and is fact-checked where appropriate. Learn more about why you can trust DayTrading.com



