Forex Trading On Margin



Forex trading on margin accounts is the most common form of investing in currencies. This tutorial explains what ‘margin’ is and how to use it when trading forex online.
Quick Introduction
- Margin is the amount of money you must front as a deposit to open a position with a forex broker
- You can leverage this capital to increase your buying power and profits or losses
- The margin essentially acts as a security deposit for the forex broker
- Understanding margin requirements, and how leverage levels affect them, is a key part of trading currencies successfully
Best Brokers For Forex Trading On Margin
These are the 4 top brokers for forex trading on margin based on our experts' findings in December 2025:
What Is Margin In Forex Trading?
Opening a forex margin account involves borrowing money from a broker to gain a greater potential return on investment (ROI).
This enables currency traders to control a larger position than their own invested capital would.
The size of the loan is equal to the amount of leverage the forex trader takes on.
The core meaning of leverage is the ability to control large amounts of money using very little of your own capital and borrowing the rest.
Leverage is expressed in ratios, and is defined from the outset when you choose the amount of capital you wish to control.
If the client’s position worsens and a loss looks likely, the firm may issue a margin call. This usually means the forex trader is instructed to either deposit more money or close out their position.
The purpose of this is to minimize the risk to both parties.
How A Margin Trade Works
A currency trade cannot be placed until the user deposits money into their forex margin account. The amount that must be deposited depends on the margin percentage that is agreed for the leverage.
The brokerage uses this deposit to maintain your position. Margin deposits are usually taken from forex traders and pooled together for a fund to place trades within the interbank network.
Margin will typically be expressed as a percentage of the full amount of a position. The majority of forex day trading platforms will require anything from a low margin of 0.25%, 0.5%, 1% or 2% up to higher-level margins.
The margin your forex broker requires enables you to work out the maximum leverage available to you in your account.
Let’s say your trading brokerage requires a 1% margin to control a $100,000 position. This will mean that your forex broker sets aside $1,000 from your account, and the remaining $99,000 will be supplied as leverage.
This is a margin of 1% and a leverage of 1:100, and you are using the margin to control currency to the sum of $100,000. That $1,000 deposit you contribute is the margin you give in order to be free to use the broker’s leverage.
If your firm requires a 2% margin, the leverage will be 1:50. A 5% margin means leverage of 1:20, and so on.
This primary definition of ‘margin’ is common to all forex accounts, but you will probably see other margin terms on your platform:
- Used margin: This is the money the forex broker has locked in to keep your current positions open
- Usable margin: This refers to the money in your forex account that can be used to open new positions
- Margin call: This happens when the money you have in your forex account is insufficient to cover your possible loss
Interest / Rollover
No interest is directly paid on the borrowed amount, but there will be a delivery date attached, and if the forex trader fails to close their position in time then it will roll over.
In this case, there may be interest charged depending on whether the forex trader’s position is long or short, as well as the short-term interest rates of the currencies in question.
Accounts Explained
You can expect the type of account you hold with a forex broker to have an impact on the available margin and leverage.
If you hold a standard account only with a brokerage, the available leverage is likely to be considerably lower, and the margin required to secure that leverage will be higher.
This is because you are likely to be less experienced and working with smaller amounts of money than those who hold higher-level accounts, such as professional and VIP.
Forex brokers take on a certain amount of risk with every client, and when engaging in forex trading on margin the risk to the broker is higher.
There is likely to be more faith in clients who hold a higher-level account, so superior margins and leverage will be available. In short, the more premium your account type with the forex broker, the better your ratio of leverage to margin will be.
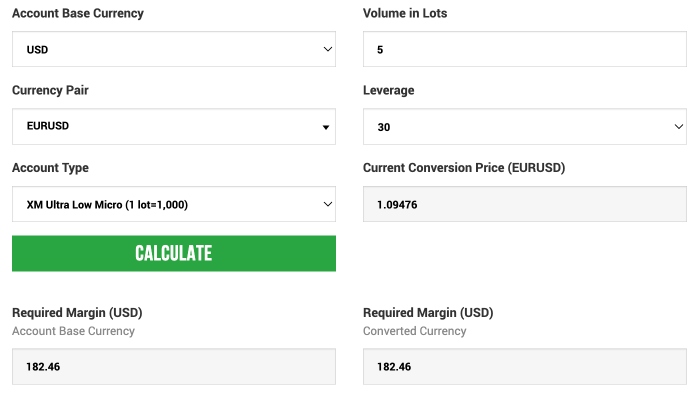
Forex Margin Calculator
One of the most important things to do when weighing up whether to start forex trading on margin is to understand how much leverage will be available for a given margin.
XM offer a great margin calculator across all currencies and forex pairs.
To work out your capital requirements ahead of currency trading on margin, here is the formula:
(Exchange rate * unit per pip) * leverage
The exchange rate is the whole number, with no decimals. The unit per pip is the amount you want to risk / make on each pip of the exchange rate movement. Leverage is the ratio that forex trading platform will offer to you – but here we need to convert it to a percentage, or decimal. So 1:10 would become 0.10, 1:30 would become 0.033 and 1:200 would become 0.005 (as examples).
Let us look at a full example.
We will trade GBP/AUD for £1 a point (pip). We will say the rate is 1.9350. The leverage will be 1:20
So our calculation is:
(19350*1) * 0.05 = 967.5
So you would need £967.5 in your forex trading account to open this position.
Let’s tweak some numbers and see what changes. Firstly, let’s be bold and risk £5 per point. Secondly, let’s use a forex broker that offers 1:200 leverage:
(19350*5) * 0.005 = 96.75
Now you need just £96.75 to open this position – even though the trade is 5 times as big at £5 per point.
The first part of the calculation is your overall exposure – the amount of currency you are buying in effect. Here is one last example:
Here we are trading BTC/GBP – Bitcoin – again, £1 a point, this time with leverage of 1:2 (This is the level most EU brokers will offer on cryptocurrency). We will say the exchange rate is 9650:
(9650*1) * .5 = 4825
So here, we need to put down far more capital than a major forex pair. This reflects the volatility and risk the forex broker is taking, effectively lending money on this asset.
We have used GBP in the examples, but the same formula and calculation applies whether trading EUR, USD or any other currency.
Margin Call In Forex
We have mentioned before that a margin call is something forex traders want to avoid happening at all costs. Let’s take an in-depth look at what it means and why you don’t want it to happen when forex trading on margin.
Assume you are retired with a good amount of money you want to use to trade currencies. You open an account with a forex broker and deposit $10,000.
When you log in, that $10,000 appears in the Equity column in your Account Information.
You see that there are also columns for Used and Usable Margin – the amount under Usable Margin is always equal to your Equity minus the Used Margin. Equity, rather than Balance, is used to determine your usable margin, and it will also determine whether or not a Margin Call occurs.
Simply put, as long as you keep your Equity higher than your Used Margin, a Margin Call will not occur. As soon as Equity is equal to or lower than the Used Margin, you will receive a margin call.
Imagine your margin requirement is 1%, and you decide to purchase 1 lot of GBP/USD. Your Equity will remain at $10,000, and your Used Margin will now read $100.
The Usable Margin now stands at $9,900.
If you sell back that 1 lot of GBP/USD at the same price you bought it at, the Used Margin would return to $0 and Usable Margin would go back to $10,000.
If, however, you decided to buy a further 79 lots of GBP/USD, totalling 80, your Equity will remain the same but your Used Margin will now be $8,000.
The Usable Margin will now stand at $2,000. This risky move could yield an enormous profit if GBP/USD rises, but if it falls then you will see your Equity fall along with it.
The Used Margin will remain at $8,000, but as soon as the Equity drops below $8,000 you will have a Margin Call.
This will mean that some or all of your position will be immediately closed at the current market price. This will mean a considerable loss to you and is the reason why taking big risks is never a sensible approach when trading on margin.
Trading Forex Without Margin
When you trade forex without margin, all transactions must be made with either available cash or long positions. So whenever you buy a position without margin, you must deposit the cash required to settle the trade or sell an existing position on the same trading day.
In other words, cash proceeds must be available to settle the buy order directly – it’s a straightforward approach but somewhat limited.
Pros
- Less Risk: Forex margin trading can lead to greater profits, but it can also cause larger losses. Trading currencies without margin exposes you to less risk, and although the potential profits are smaller, with a good strategy you can make gains.
- Less Stress: Having larger positions open can be stressful and sometimes causes people to make poor decisions. The fluctuations will look much bigger with forex margin trading, while smaller positions without margin will feel safer, more secure, and ultimately less stressful.
- No Margin Calls: A margin call is the nightmare of anyone trading forex on margin. When you trade currencies without margin, there is no risk of this occurring, giving you peace of mind.
Cons
- Less Buying Power: The most obvious disadvantage of trading FX without margin is that you will be able to control less currency, and thus your buying power is far lower. By borrowing from your forex broker, you can control significantly larger positions and boost your potential profits by a huge amount.
- Less Flexibility: By having less capital at your disposal, you will have less flexibility to quickly build a portfolio. If your account only enables you to take up 1 position at a time, it is going to take a long time and work to build up a portfolio. Forex trading on margin opens up more doors, giving you the flexibility you need to diversify your portfolio.
- Limited Account Growth: Before margin came into the equation, small forex traders found it difficult to grow their accounts rapidly. By being limited to your account balance, you will probably have to focus on slow and steady growth over a long period, whereas forex trading on margin gives you the power to grow at a faster rate with a relatively small investment from your own funds.
- More Personal Capital Required: Without leverage from your forex broker, you are going to need to invest more of your own money to see the profits you need to grow and sustain your career as an investor. The forex margin required by firms can be very small, giving you access to a large fund that you can use to grow and secure your trading future.
Though the risks are greater, the potential gains associated with forex trading on margin are what make it a good choice for many investors.
Trading forex without margin is restrictive, and though you can make a success of it, you will likely be in for a much slower and longer journey to where you want to be.
FAQs
What Is Margin In Forex?
Margin is the money you must deposit with a forex broker to borrow money, thus increasing your purchasing power and potential profits.
Margin trading is popular with currency traders and offered by many of the best forex trading platforms and brokers.
Is Trading Forex With Margin Safe?
Margin trading on forex is risky. Whilst your returns are magnified so too are losses.
As such, make sure you take a proactive approach to risk management.
Article Sources
The writing and editorial team at DayTrading.com use credible sources to support their work. These include government agencies, white papers, research institutes, and engagement with industry professionals. Content is written free from bias and is fact-checked where appropriate. Learn more about why you can trust DayTrading.com



