CFD Trading In China



China’s financial markets have snowballed, and despite Chinese government restrictions, contracts for difference (CFDs) have become a popular choice for active traders who want to get involved in the markets.
If you’ve ever wondered how to trade the rise or fall of China’s vast markets without buying a single stock or commodity, this beginner’s guide will help you understand the ins and outs of CFD trading in China.
Quick Introduction
- CFDs let traders speculate on price movements of stocks, commodities, indices, and even forex without owning the underlying assets. In China, this is particularly attractive as it allows access to volatile markets without the complexities of asset ownership.
- China has strict financial regulations, and the CFD market is no exception. CFDs are not directly available to Chinese residents, but offshore platforms allow access. Traders must be mindful of local rules and choose regulated, trustworthy brokers.
- CFD trading in China offers leverage, meaning traders can control larger positions with a smaller initial investment. While this increases potential profits, it also amplifies risks, especially in the fast-moving Chinese markets.
- As China’s economy continues to expand and diversify, interest in CFDs has grown among international traders. CFDs offer an efficient way to tap into China’s emerging sectors without long-term commitment.
Best CFD Brokers In China
After direct testing, we've found these 4 CFD trading platforms that accept China traders the best:
How Does CFD Trading Work?
CFDs allow you to trade Chinese, other Asian and global financial markets without the added expense of owning the actual assets. This makes them a financial derivative.
Leverage allows you to open larger positions while committing a fraction of the total value or margin needed to, for example, buy the equivalent amount of shares listed on Chinese stock markets.
To explain how it works, let’s examine a potential trading opportunity on a stock market index: FTSE China A50 (FTXIN9). The components are chosen each quarter from the 50 largest companies on the Shanghai Stock Exchange and Shenzhen Stock Exchange, which issue A-shares; B-shares are not included.
If you’re convinced the index will rise, you’d buy a CFD position in the FTXIN9. If each contract is valued at 13,500, and your brokerage requires a 5% margin, then to take a position on 10 contracts, you’d need a margin of CNY 6,750 (13,500 per contract x 10 contracts x 5%).
If the China A50 rises to 13,600, the price increase would yield CNY 100 per contract. By closing your position, you would bag a total profit of CNY 1,000 (10 contracts x CNY 100), excluding broker fees. But, if the index falls to 13,400, you would lose CNY 1,000.
This highlights the risks involved with CFD trading; you can control significant size with leverage, but gains and losses are increased.
Understanding how margin and leverage work is critical to your future trading success.If you are new to CFD trading, thinking about opening a demo trading account. It’s a terrific introduction to practice strategies and can help you build confidence before you risk your yuan in the markets.
What Can I Trade?
CFD trading in China offers a wealth of trading opportunities spread across various financial markets, both in China and internationally:
- Stock CFDs – You can trade individual Chinese shares listed on the Shanghai Stock Exchange and Shenzhen Stock Exchange without the extra expense of buying the shares. Alternatively, you could trade stocks from other exchanges like the Australian Securities Exchange (ASX).
- Index CFDs – The FTSE China A50 (FTXIN9) is China’s leading share market index. It is a market capitalization-weighted index composed of the top 50 listed companies on the Shanghai Stock Exchange and Shenzhen Stock Exchange. Traders choose index CFDs to speculate on a stock exchange’s overall market performance rather than deal in individual shares. As an alternative, you could consider CFDs on global indices like the Dow Jones or FTSE. Liquidity is always high on these indices, and trading costs are usually very competitive.
- Forex CFDs – The CNY is traded domestically and the CNH is more so in the global foreign exchange market. Popular currency pairs include USD/CNY and EUR/CNY. These pairs are high in liquidity and can provide opportunities for short-term currency traders.
- Commodity CFDs – Vital commercial commodities like crude oil (China is the largest importer) and copper (crucial to China’s huge manufacturing industry) can be traded as CFDs.
- Crypto CFDs – Some Chinese residents may have a fascination with trading digital tokens like Bitcoin and Ethereum, however the Chinese government banned crypto assets in 2021. Some offshore brokers may offer crypto CFDs, but they remain high-risk due to large price swings.
Is CFD Trading Legal In China?
CFD trading is a legal grey area for retail investors within mainland China.
The China Securities Regulatory Commission (CSRC) oversees financial markets but has not approved the offering of CFD products by domestic financial institutions. So, you won’t find local Chinese brokers offering CFDs to retail investors.
Chinese traders can still access CFDs through international brokers in regions like Hong Kong, Singapore, and Europe. Technically, Chinese authorities don’t regulate offshore brokers directly, but they don’t explicitly endorse or allow domestic residents to use them.
Using offshore platforms to trade CFDs poses certain risks. First, if disputes arise, you may not be protected under Chinese law since offshore brokers operate under different regulatory bodies.
Additionally, access to such platforms could be blocked if the government tightens regulations, as China has previously restricted access to foreign financial services websites.
While mainland China has restrictions, Hong Kong operates under a different regulatory regime. Some Chinese traders leverage brokers based in Hong Kong to access CFD markets legally through this unique administrative region. But again, this is a workaround, not a direct approval for mainland traders.
Is CFD Trading Taxed In China?
Since CFD trading is not directly legal for retail traders within mainland China, there are no formal tax rules explicitly targeting profits from CFD trading inside the country.
However, all income Chinese residents earn is taxable under the country’s individual income tax (IIT) rules, including those from speculative financial products, which could theoretically be subject to taxation.
If Chinese residents trade CFDs through offshore brokers, they are not taxed directly at the source because such brokers typically operate under foreign tax jurisdictions.
However, Chinese tax law stipulates that citizens must report all global income, which technically includes profits from trading CFDs on foreign platforms.
China’s income tax system has a progressive rate that can reach 45% depending on income. However, the lack of clear guidelines or enforcement on foreign investment income makes it difficult to know how strictly this rule is applied to CFD trading profits.
One area of uncertainty is how CFD profits are classified under Chinese tax law. Traditionally, CFD gains may not be considered “capital gains” since traders do not own the underlying asset but instead speculate on price movements. The profits might fall under a broader “investment income” category.
However, a flat rate of 20% is applied to many remaining forms of individual income in China, including dividends and capital gains, unless specifically reduced by the State Council, according to PwC.
Chinese residents should report their trading profits to the tax authorities and pay the applicable taxes on these gains.Given the complex legal and tax landscape in China, speaking to a tax professional is a sensible course of action.
An Example Trade
To bring CFD trading in China to life, I’m focusing on the FTSE China A50 index as an example.
An index can theoretically reveal the strength of an individual country’s economy at any given time. In some ways, it’s similar to trading FX pairs, including the domestic currency.
When trading an index, I’ll apply fundamental analysis and technical analysis. Regarding fundamental analysis, I’ll examine my economic calendar to determine whether any key metrics concerning the country’s financial landscape have been published or are about to be published.
For example, unemployment, export/import figures, inflation, government debt and borrowing, GDP growth, etc. If any metrics miss or beat the analysts’ expectations, this could be bullish or bearish for an index.
I’ll also scour newswires for articles indicating economic sentiment regarding the country. Several free finance sites provide excellent commentaries on how a country’s economy is performing. Google Finance and Yahoo Finance are superb resources, as are Investing.com and Tradingeconomics.com.
Technical Analysis
If you’re day or swing trading an index, you should select a lower time frame, like the 1-hour (1HR) or 4-hour (4HR), that reflects your timescale for making a decision and banking potential profit. There’s no point in analyzing the weekly or monthly timeframe if you want to enter and exit on the day.
I’m also mindful that if I’m looking to execute a day trade, I have to be able to look at a chart and make a quick decision. Therefore, I don’t clutter my charts with too much information; I limit it where possible. At most, I’ll plot four indicators on my chart and utilize one from each set: volume, trend, momentum, and volatility.
My go-to indicators are the MACD, RSI, stochastic oscillator, PSAR, Bollinger Bands, and exponential moving average crossovers.But I won’t use all six as it’s overkill in many situations; duplication is possible, and Heikin Ashi candlesticks can illustrate the price action I want to identify. Instead, I’ll select one or two indicators that work well on indices and lower timeframes.
In this instance, I’m using the RSI and a stochastic oscillator. I should be able to see overbought and oversold conditions, turning points, and an increase or decrease in volatility if a trend is developing and has momentum.
1-Hour Timeframe
In the below chart, after the bearish sentiment exhausts, we can see the formation of a textbook Doji candlestick. After that, we witness the creation of positive bullish candles as price prints higher highs. What follows is a ranging period, which became my cue for exiting.
My chosen indicators also supported my decision to enter once the bullish candle formed after the Doji; the stoch and RSI indicated an oversold market, and the RSI indicated a quick shift in momentum as the reading quickly breached the median 50 line.
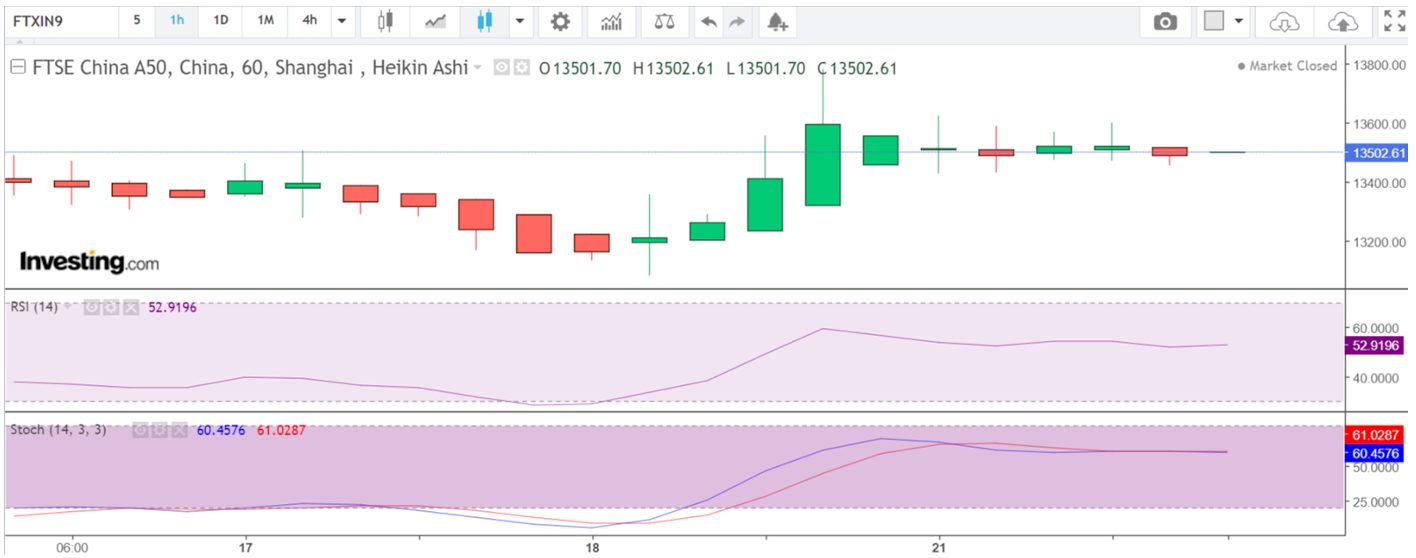
My signal to enter was the crossing of stochastic lines combined with the bullish candle forming after the doji was fully formed. I entered at 13,200 and exited automatically at 13,500 when the market began to range.
Bottom Line
In China, retail traders can’t legally access CFDs through local brokers. The government has tight regulations, so CFDs aren’t offered directly in mainland China.
Despite the restrictions, many traders in China use offshore brokers to trade CFDs. While it’s doable, it’s a bit of a legal minefield, and the platforms aren’t regulated by Chinese authorities, which means added risks.
CFDs let you trade with leverage, which means you can control a bigger position with a smaller investment. However, remember that while this boosts potential profits, it also increases risk, especially in China’s fast-moving markets.
Technically, profits from CFD trading should be reported for taxes under China’s global income rules, but enforcement is a bit patchy regarding offshore trading.
So, if you’re considering CFD trading in China, proceed with caution, stay informed about the rules, and pick a trustworthy broker.
To get going, utilize DayTrading.com’s choice of the best CFD day trading platforms.
Recommended Reading
Article Sources
- FTSE China A50 (FTXIN9)
- Shanghai Stock Exchange
- Shenzhen Stock Exchange
- China Securities Regulatory Commission (CSRC)
- Economic Calendar - Trading Economics
- Individual - Taxes on Personal Income - PwC
The writing and editorial team at DayTrading.com use credible sources to support their work. These include government agencies, white papers, research institutes, and engagement with industry professionals. Content is written free from bias and is fact-checked where appropriate. Learn more about why you can trust DayTrading.com



