Accumulator Options



Accumulator-style options (as offered by brokers like Deriv) are short-term derivative contracts that pay compounded returns if an underlying index price stays within a barrier range over a set number of ticks. These differ from traditional structured accumulators, which involve periodic delivery of underlying shares at a fixed strike. Always review your broker’s product specifications.
This guide will explain what these securities are, walk through an accumulator option trade, and discuss the pros and cons of trading them.
Quick Introduction
- Accumulator options are bets on the stability of an asset’s price over a specified timescale.
- These derivatives establish a price range within which the asset must remain for traders to profit.
- They can be used for a variety of purposes, from speculating on short-term price movements to hedging risk.
Best Broker With Accumulator Options
Deriv is emerging as the best accumulator options broker for day traders, with 1-5% growth rates, durations up to 230 ticks, and integrated risk management tools.
Accumulators are available on all of Deriv’s bespoke volatility indices, with trade sizes from $1 to $100.
You can also trade accumulators on both the intuitive DTrader platform and mobile app.
Minimum Deposit: $5
Regulators: MFSA, LFSA, BVIFSC, VFSC, FSC, SVGFSA
What Are Accumulator Options?
Accumulator options involve a series of transactions between a trader and an online broker. They allow individuals to profit from the sideways movement of an asset if the price remains within predefined levels.
The accumulator structure consists of a series of knockout options. These barrier options allow the trader to buy (accumulate) a specific amount of an underlying asset at a certain strike price within that specified timeframe.
Decumulator options work in the opposite way, allowing traders to sell (decumulate) a defined quantity of an underlying security at a particular price within a set period.
Provided that the underlying asset does not break through the knockout barrier, the trader accumulates the agreed quantity of said asset in stages until the end of the period.
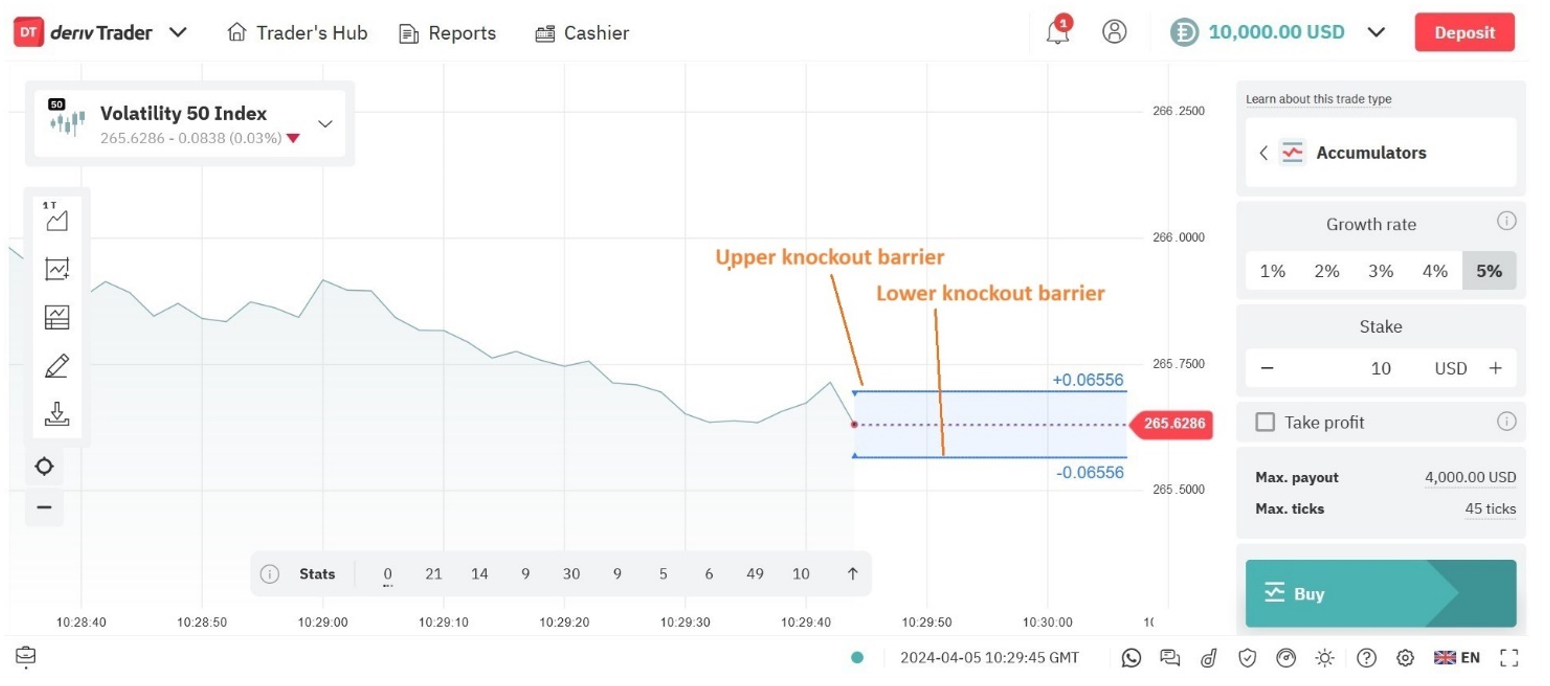
The trader can sell the underlying security once each option is exercised. However, if the spot price hits or breaks through the upper or lower barrier, the trade automatically closes. Any such breach of the knockout threshold will see the trader lose any unrealized profits, along with their initial stake.
With these products, traders select a growth rate based on their investment goals. Their potential profits will compound incrementally based on this rate, as long as the spot price of the underlying asset stays within the specified range from the previous price.
A higher growth rate can magnify profits, though on the flipside a greater rate carries greater trading risk. This is because the risk of the underlying security breaching the range boundaries is greater.
An Accumulator Trade In Action
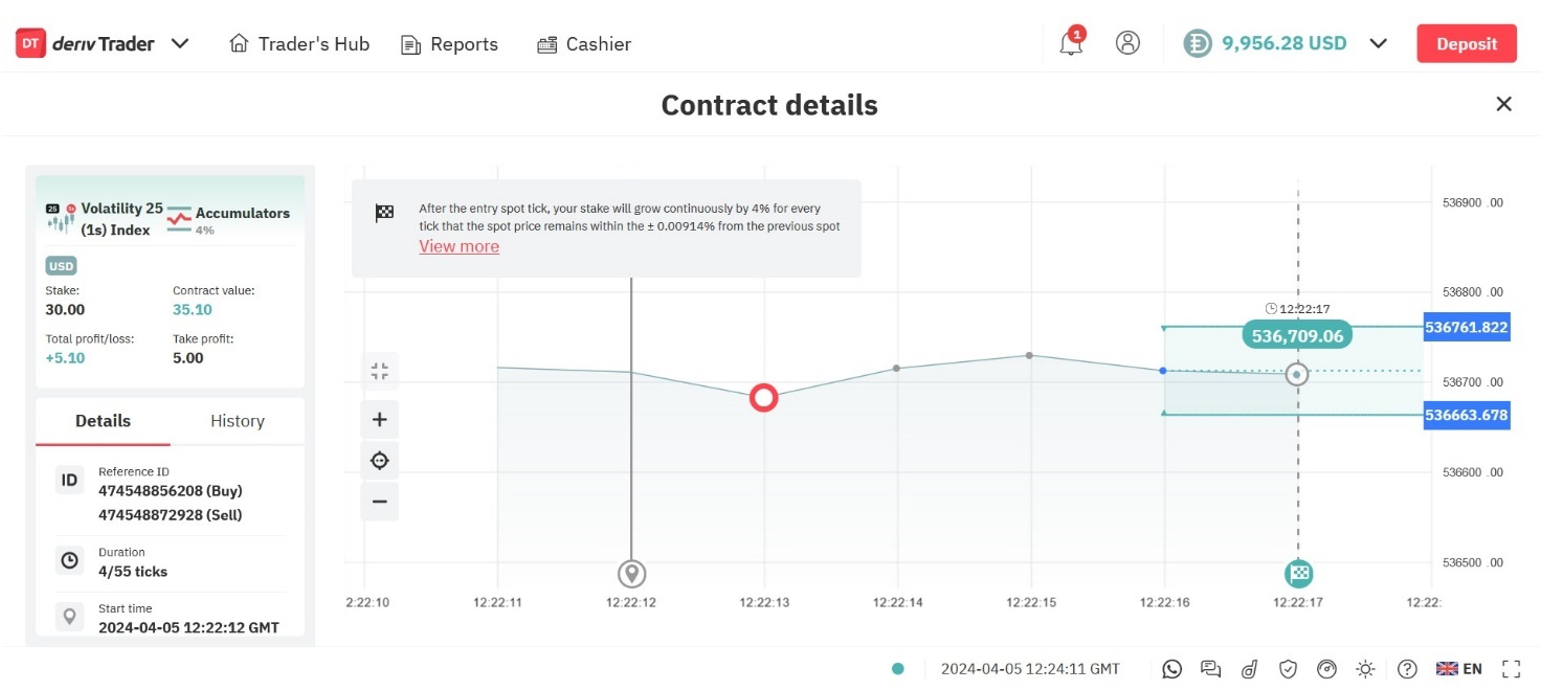
Let’s say that I decide to trade accumulator options using Deriv.
From the range of volatility indices, I select the Volatility 25 (1s) Index, which is based on a simulated market with a constant volatility of 25%. With this index, one tick is generated every second.
The next step is to choose a growth rate, which with Deriv ranges between 1% and 5%. I decide to take a little extra risk so choose an accumulator with a 4% growth rate. At this level, the contract automatically closes out after 55 ticks (or seconds).
I then choose to make a $30 stake, and set a take profit order of $5 to reduce my risk. Once my profit reaches or exceeds this amount, the trade is automatically closed and my earnings are booked.
After five ticks, the contract reaches $35.10 and the trade is closed. My take profit instruction has been triggered and I’ve realized a $5 profit.
Pros And Cons Of Trading Accumulator Options
Pros
- Not dependent upon volatility – Short-term traders can generate healthy profits when financial markets are trading in tight ranges, unlike many derivative products that rely on sharp price movements.
- Multiple uses – These derivatives can be used for a variety of purposes, including speculation, income generation and potentially hedging in certain circumstances.
- Flexibility – Traders can close out their contract whenever they choose (provided that knockout barriers have not been breached).
- Trading around the clock – The volatility indices that can be traded with accumulators are open 24/7, giving traders wider choice on when they wish to do business, notably at the weekend.
Cons
- Complexity – Accumulators are more complicated than certain other financial instruments, which in turn may make them unsuitable for inexperienced traders.
- Low availability – Accumulator options are not widely available, limiting your choice of brokers and markets if you want to trade these derivatives.
- Counterparty risk – As with all derivatives, these products leave traders vulnerable to the danger that the counterparty (i.e. the broker) defaults on their financial obligations.
Bottom Line
Accumulator options offer the potential for high rewards, but as with many financial derivatives they also involve traders taking on greater risk than they would with many other instruments. If prices begin to fluctuate, a trader can lose money rapidly as knockout barriers are breached.
For this reason, trading of these instruments is not allowed in certain territories, notably the US, the UK and the EU, all of which have laws controlling the types of financial instruments available to retail investors. Investors who wish to trade accumulators should carry out extensive research and establish tight risk management.
Our top-rated broker with accumulator options, Deriv, also offers a demo account where you can practice trading these contracts.
